| CPC H02J 50/12 (2016.02) [H01F 38/14 (2013.01); H02J 50/005 (2020.01); H01F 27/25 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
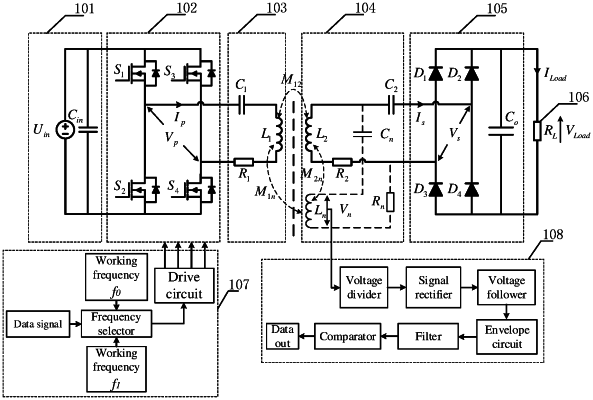
1. A wireless synchronous transmission system of energy and signal based on an integrated magnetic circuit coupling structure, comprising a direct current power supply, a high-frequency inverter circuit, a primary energy transmitter circuit, a secondary receiver circuit, a rectifier circuit, a load, a signal modulation circuit and a signal demodulation circuit, wherein
the high-frequency inverter circuit has an input terminal connected to the direct current power supply, and an output terminal connected to the primary energy transmitter circuit, the high-frequency inverter circuit is connected to the signal modulation circuit, and the signal modulation circuit is configured to control an operating frequency of the high-frequency inverter circuit;
the secondary receiver circuit comprises a secondary energy receiver circuit and a secondary signal receiver circuit, the secondary energy receiver circuit is connected to the secondary signal receiver circuit, the primary energy transmitter circuit is connected to the secondary energy receiver circuit and the secondary signal receiver circuit through electromagnetic induction, an output of the energy receiver circuit is connected to the rectifier circuit, the rectifier circuit outputs a direct current power and transmits the direct current power to the load, and the secondary signal receiver circuit is connected to the signal demodulation circuit;
the high-frequency inverter circuit converts a direct current power output from the direct current power supply into a high-frequency alternating current, the high-frequency alternating current forms a high-frequency sine wave after passing through the primary energy transmitter circuit, the high-frequency sine wave acts on the primary energy transmitter circuit, and the primary energy transmitter circuit transmits energy to the secondary energy receiver circuit and transmits a signal to the secondary signal receiver circuit through electromagnetic induction;
a working resonance point of the secondary energy receiver circuit is set to a first harmonic frequency of the high-frequency sine wave, to realize energy transmission; and
a working resonance point of the secondary signal receiver circuit is set to a third harmonic frequency of a sine wave, to realize signal transmission.
|