| CPC G06F 30/28 (2020.01) [G06N 7/01 (2023.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
4. A method for predicting a liquid phase interfacial tension between benzene and water, implemented by a computer, comprising:
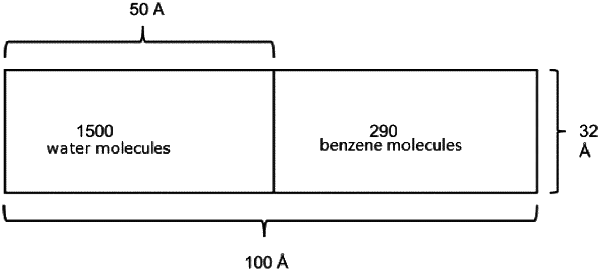
Step A: initializing the molecular simulation: two simulation boxes were prepared, both with the size (30×30×45 Å)-(35×35×55 Å), and 1200-2000 water molecules were put on the grid point of the first box, 230-380 benzene molecules were put on the grid point of the second box; then, the simulation temperature T and pressure p were set;
Step B: selecting the force field used for simulation: the TraPPE force field was used for benzene molecules, and the TIP4P/2005 force field was used for water molecules;
Step C: performing Monte Carlo simulations on the two boxes separately under a canonical ensemble, the Monte Carlo simulation containing at least one Monte Carlo move;
Step D: joining the water box and the benzene box along the z direction to form a large box of (30×30×90 Å)-(35×35×110 Å), and run the Monte Carlo simulation mentioned in the step C for 50000-80000 Monte Carlo cycles to reach equilibrium, wherein reaching equilibrium is determined if at least one given property fluctuate around a certain value as the simulation is running; and
Step E: after reaching equilibrium, running the Monte Carlo simulation under an isothermal-isobaric ensemble for 400000-500000 Monte Carlo cycles so as to obtain an interfacial tension for every 5 Monte Carlo cycles, and obtain a liquid phase interfacial tension between benzene and water according to the calculated interfacial tensions;
wherein the Monte Carlo move comprises:
(1) randomly selecting a molecule;
(2) randomly selecting a Monte Carlo move; types of move here include translation and rotation, and each type of the moves was given a selection probability of 20-40%;
(3) moving the selected molecule according to the selected Monte Carlo move to generate a new conformation;
(4) obtaining energy of the new conformation, including an intramolecular energy, an intermolecular van der Waals energy, an intermolecular short-range Coulomb energy, and an intermolecular long-range Coulomb energy; and
(5) determining, according to the energy of the new conformation, whether the new conformation is accepted.
|