| CPC G05D 1/028 (2013.01) [G05D 1/0088 (2013.01); G05D 1/0238 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
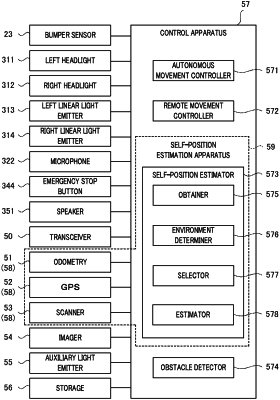
1. A self-position estimation apparatus for estimating a self-position of a mobile object, the self-position estimation apparatus comprising:
N types of sensors (where N is a natural number equal to or greater than two) that detect information with different contents from each other regarding a moving status of the mobile object;
an environment determiner that determines an environment around the mobile object;
a selector that selects information detected by one or more but less than the N types of sensors based on a determination result of the environment determiner; and
an estimator that estimates the self-position of the mobile object based on the information selected by the selector, wherein:
the N types of sensors include a radio position information detector that detects information regarding a position of the mobile object and transmitted via radio, and a scanner that scans around the mobile object,
the environment determiner determines whether the mobile object is located in a first area or a second area, the first area being an area where estimation accuracy of the self-position based on information detected by the scanner is less than a threshold value, the second area being an area where the estimation accuracy of the self-position is equal to or greater than the threshold value, and
the selector selects the information detected by the radio position information detector when the mobile object is located in the first area, and selects the information detected by the scanner when the mobile object is located in the second area.
|