| CPC G05B 23/0281 (2013.01) [G05B 19/406 (2013.01); G05B 23/0272 (2013.01); G05B 23/0275 (2013.01); G06N 3/042 (2023.01); G06N 3/045 (2023.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01); G06N 5/022 (2013.01); G06N 5/041 (2013.01); G06N 7/01 (2023.01); G05B 2219/33284 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
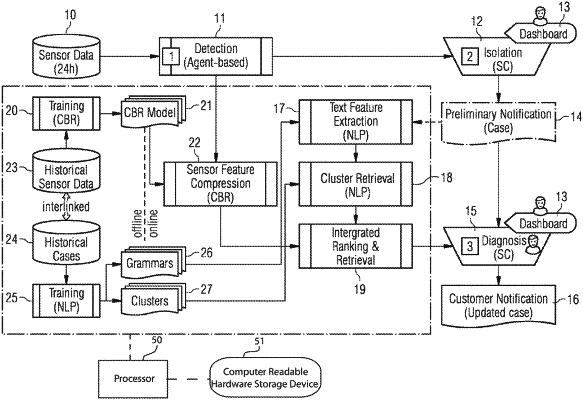
1. A method for optimizing diagnostics of rotating equipment, comprising:
providing status information about a status of the rotating equipment over a series of time windows wherein the status is derived from sensor measurements of at least one available sensor taking measurements during a predefinable time period,
identifying a given case of the rotating equipment and generating a sensor feature vector for the given case using deep learning which combines provided historic sensor information with sequence of events data indicating warnings and/or alerts of the rotating equipment, wherein deep learning uses a case-based reasoning learning method, wherein status information is supplemented with via deep learning predicted probabilities whether a warning and/or an alert has occurred within a time window of the series of time windows, and wherein said deep learning automatically identifies latent structure that makes two time windows of the series of time windows similar or dissimilar in order to predict the probabilities,
providing an amount of historic textual diagnostic knowledge cases,
extracting semantic information on text features from the historic textual diagnostic knowledge cases and from the given case, wherein a natural language training method is used for extracting said semantic information,
determining a text feature vector for the given case, and
combining the sensor feature vector for the given case and the text feature vector for the given case into a unified representation enabling optimization of the diagnostics, wherein the unified representation is one unified feature vector.
|