| CPC G01W 1/10 (2013.01) [G01W 2001/006 (2013.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
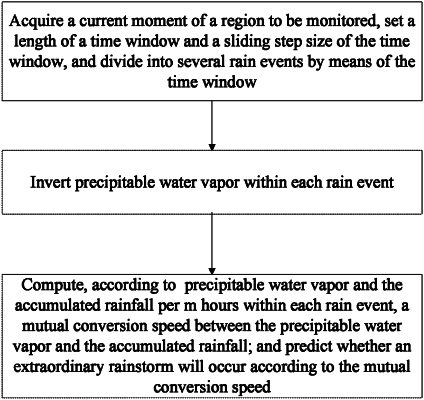
1. A method for monitoring an extraordinary rainstorm based on multi-source data, comprising:
acquiring a current moment of a target region; assuming that an initial monitoring moment of the target region is t1 and the current moment of the target region is t2; setting a length of a time window as L and a sliding step size of the time window as L/2; and dividing a time period t2−t1 into n rain events by means of the time window, wherein n is a positive integer;
inverting precipitable water vapor (PWV) within each rain event; wherein
the inverting precipitable water vapor within each rain event comprises:
acquiring observational data and meteorological data collected by a global navigation satellite system in the target region; performing accuracy verification on the meteorological data collected by the global navigation satellite system;
and inverting the precipitable water vapor according to the observational data and the meteorological data; wherein
the performing accuracy verification on the meteorological data collected by the global navigation satellite system comprises:
collecting data from a meteorological station, and obtaining meteorological data for the meteorological station by performing elevation conversion on the data from the meteorological station;
collecting data from the fifth generation european centre for medium-range weather forecasts atmospheric reanalysis of the global climate (ERA5), and obtaining meteorological data and precipitable water vapor for the ERA5 by performing elevation conversion and bilinear interpolation on the data from the ERA5;
computing a first difference between the meteorological data collected by the global navigation satellite system and the meteorological data for the meteorological station;
computing a second difference between the meteorological data collected by the global navigation satellite system and the meteorological data for the ERA5;
indicating, if the first difference and the second difference are both within a predetermined range, that the meteorological data collected by the global navigation satellite system passes accuracy verification; and otherwise, indicating that the meteorological data collected by the global navigation satellite system fails to pass accuracy verification, and recollecting data from the global navigation satellite system;
acquiring an accumulated rainfall per m hours within each rain event, wherein m is a positive integer; computing, according to precipitable water vapor and the accumulated rainfall per m hours within each rain event, a mutual conversion speed V between the precipitable water vapor and the accumulated rainfall; indicating, if the mutual conversion speed is greater than or equal to 1, that a rainfall is excessive and the extraordinary rainstorm is going to occur after the current moment; and indicating, if the mutual conversion speed is less than 1, the rainfall is insufficient and the extraordinary rainstorm is about to end; wherein
the computing, according to precipitable water vapor and the accumulated rainfall per m hours within each rain event, a mutual conversion speed V between the precipitable water vapor and the accumulated rainfall comprises:
measuring the mutual conversion speed V between the PWV and the rainfall according to a number of refills for PWV (NRPWV), which is calculated as follows:
 wherein n is a number of PVWs in a predetermined time period, and PRE is a total rainfall in the predetermined time period.
|