| CPC G01P 3/44 (2013.01) [G01C 19/5649 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
1. An inertial measurement device comprising:
an angular velocity sensor;
an acceleration sensor; and
a micro controller unit that controls the angular velocity sensor and the acceleration sensor;
wherein the angular velocity sensor comprises:
three mutually orthogonal axes being defined as an X-axis, a Y-axis, and a Z-axis;
a substrate; and
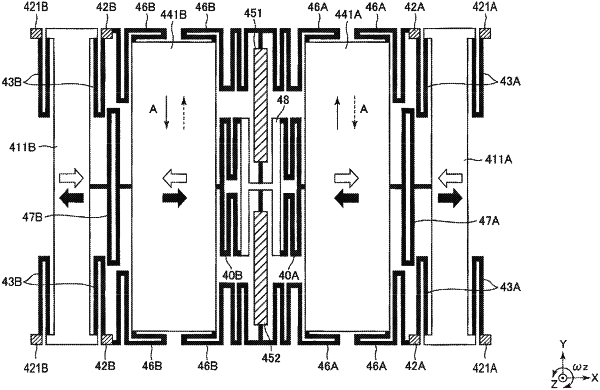
an element section that is supported on the surface of the substrate orthogonal to the Z axis and detects an angular velocity based on a change in capacitance, wherein
the element section comprises:
a first electrode including a first trunk part extending in a Y-axis direction along the Y-axis, and a plurality of first electrode fingers extending in an X-axis direction along the X-axis from an edge portion of the positive side of the X-axis of the first trunk part; and
a spring extending in the Y-axis direction, wherein
the first trunk part includes a first surface adjacent to the spring at an edge portion of the negative side of the X axis; and
in a plan view from a Z-axis direction along the Z-axis, a distance between one end side of the first surface and the spring is different from a distance between the other end side of the first surface and the spring.
|