| CPC C25B 3/25 (2021.01) [C07C 51/15 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
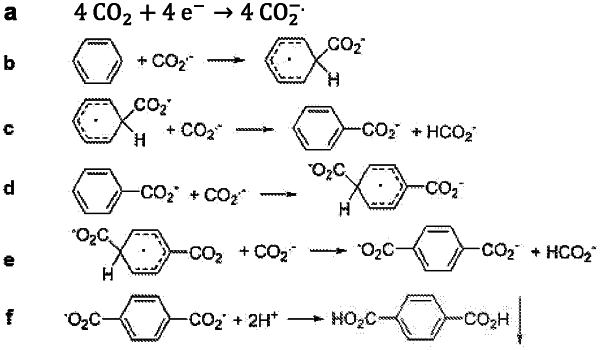
1. A method for electrochemical reductive carboxylation of an unsaturated organic substrate, the method comprising:
(a) providing a reactant medium comprising a water-immiscible, ionically conductive, aprotic organic liquid comprising an ionic liquid comprising one or more ionic liquid cations and one or more ionic liquid counter anions, an unsaturated organic substrate reactant, and a carbon dioxide reactant, wherein the reactant medium is free from cation electrolytes other than the one or more ionic liquid cations;
(b) providing a product medium comprising water;
(c) electrochemically reducing the unsaturated organic substrate reactant in the reactant medium with (i) a cathode in the reactant medium and (ii) an anode in the product medium, thereby forming a dicarboxylic organic product comprising a reaction product between (i) at least one of the unsaturated organic substrate reactant and a radical-anion of the unsaturated organic substrate reactant, and (ii) at least one of carboanions formed from the carbon dioxide reactant, CO2− anion-radicals formed from the carbon dioxide reactant, and the carbon dioxide reactant in the reactant medium; and
(d) recovering the dicarboxylic organic product in the product medium after transport of the dicarboxylic organic product formed in the reactant medium to the product medium.
|