| CPC C13K 13/00 (2013.01) [B01J 4/001 (2013.01); B01J 19/0053 (2013.01); B01J 19/20 (2013.01); B01J 2219/00033 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
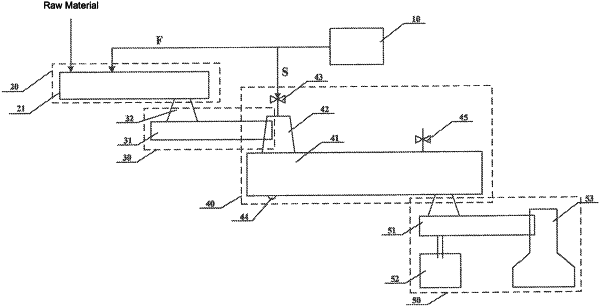
1. A device for continuously producing sugar by hydrolyzation using lignocellulosic raw material, comprising:
an acid solution output unit for outputting a first acid solution and a second acid solution respectively;
a raw material mixing unit connected to the acid solution output unit, for mixing the raw material with the first acid solution to form a mixture and continuously conveying the mixture;
a feeding unit connected to the raw material mixing unit, for receiving the mixture, compressing the mixture and conveying the mixture outward; wherein the feeding unit comprises a first tapered discharging tube connected to the raw material mixing unit and a screw feeder respectively, for receiving the mixture from the raw material mixing unit and conveying the mixture to the screw feeder;
a main reaction unit connected to the feeding unit and the acid solution output unit, for receiving the mixture and the second acid solution respectively, and sufficiently stirring and mixing the mixture with the second acid solution at a pressure higher than a normal pressure to cause them to react; and
a discharging unit connected to the main reaction unit, for performing solid-liquid separation of a resultant obtained from the reaction and outputting a product.
|