| CPC C01D 3/06 (2013.01) | 12 Claims |
|
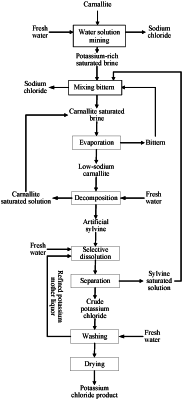
1. A method for preparing potassium chloride from a carnallite, comprising:
(1) contacting a preheated fresh water with the carnallite in a water solution mining treatment to obtain a potassium-rich saturated brine, wherein a temperature of the potassium-rich saturated brine is 40° C.-50° C.; wherein the potassium-rich saturated brine comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 7 wt %-11 wt % of NaCl, 7.5 wt %-9.5 wt % of KCl, and 11 wt %-15.5 wt % of MgCl2; a mass ratio of a fresh water to the carnallite is 0.25:1-1.20:1; in a process of the water solution mining treatment, the mass ratio of the fresh water to the carnallite is reduced by 0.15-0.20 when a content of sodium chloride in the carnallite is increased by 10 wt %;
(2) mixing the potassium-rich saturated brine, a sylvine saturated solution, and a bittern at 40° C.-50° C. for mixing brine to obtain a carnallite saturated brine and sodium chloride; wherein the carnallite saturated brine comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 1.6 wt %-1.8 wt % of NaCl, 4.0 wt %-4.5 wt % of KCl, and 26.5 wt %-27.0 wt % of MgCl2;
(3) evaporating the carnallite saturated brine at 40° C.-50° C., and then carrying out a solid-liquid separation to obtain a low-sodium carnallite and the bittern; wherein the low-sodium carnallite comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 9 wt %-10 wt % of NaCl, 20 wt %-22 wt % of KCl, and 32 wt %-35 wt % of MgCl2;
(4) carrying out a fresh water decomposition treatment on the low-sodium carnallite at 10° C.-25° C., and then carrying out the solid-liquid separation to obtain an artificial sylvine and a carnallite saturated solution, wherein the artificial sylvine comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 25 wt %-30 wt % of NaCl and 70 wt %-75 wt % of KCl; and
(5) carrying out a selective dissolution treatment on the artificial sylvine with the fresh water at 10° C.-25° C. to obtain a crude potassium chloride and a statured sylvine solution, and then refining to obtain a potassium chloride; wherein a mass ratio of the fresh water to the artificial sylvine is 0.7:1-1:1.
|