| CPC A61B 5/395 (2021.01) [A61B 5/1107 (2013.01); A61B 5/726 (2013.01); A61B 5/7221 (2013.01); A61B 5/742 (2013.01); A61B 5/746 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
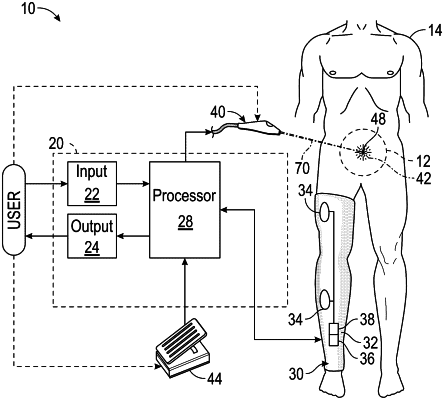
1. A method of alerting a user to the existence of an artificially induced neuromuscular response in a subject, the method comprising:
generating a mechanomyography (MMG) output signal corresponding to a mechanical motion of a muscle of a subject, the generating performed by a mechanical sensor in physical communication with the muscle;
applying a wavelet transform to the MMG output signal to determine a convolution coefficient for each of a plurality of daughter wavelets, wherein each daughter wavelet of the plurality of daughter wavelets is a time-scaled variant of a common mother wavelet, and wherein the convolution coefficient is indicative of a similarity between the daughter wavelet and the MMG output signal;
summing the convolution coefficients determined across the plurality of daughter wavelets at each timestep across a plurality of timesteps to generate a net-convolution coefficient (NCC) that varies across the plurality of timesteps;
identifying one or more peaks in the NCC via a peak finding algorithm;
determining a minimum stimulus current required to result in an identified peak in the NCC, the determining comprising:
transmitting an electrical stimulus to an electrode of a selectively electrifiable nerve stimulator, the nerve stimulator operative to apply an electrical stimulus to a nerve or nerve root during a surgical procedure, the electrical stimulus comprising a plurality of discrete electrical pulses, each having a current magnitude greater than the minimum stimulus current required to result in an identified peak in the NCC;
identifying a plurality of peaks in the NCC corresponding to the transmitted electrical stimulus, the plurality of peaks in the NCC having a periodicity that is about equal to a periodicity of the plurality of discrete electrical pulses;
transmitting an electrical stimulus comprising a second plurality of discrete electrical pulses following the identification of the plurality of peaks, wherein each discrete electrical pulse in the second plurality of discrete electrical pulses has a different current magnitude; and
wherein the current magnitude of each of the discrete electrical pulse in the second plurality of discrete electrical pulses is selected to identify a current sub-range that contains the minimum stimulus current, wherein the current sub-range is defined by a first current magnitude lower than the minimum stimulus current and a second current magnitude that is greater than the minimum stimulus current; and
wherein the minimum stimulus current includes a current magnitude selected from the identified current sub-range;
alerting a user of an artificially induced neuromuscular response following the identification of one or more peaks in the NCC: and
displaying the minimum stimulus current to the user.
|