| CPC A61B 5/0036 (2018.08) [A61B 5/0035 (2013.01); A61B 5/0064 (2013.01); A61B 5/0071 (2013.01); A61B 5/0075 (2013.01); A61B 5/055 (2013.01); A61B 5/441 (2013.01); A61B 5/4504 (2013.01); A61B 5/4887 (2013.01); A61B 5/7235 (2013.01); A61B 6/032 (2013.01); A61B 6/485 (2013.01); A61N 5/1049 (2013.01); A61N 2005/0626 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A method for obtaining anatomical information, said method comprising:
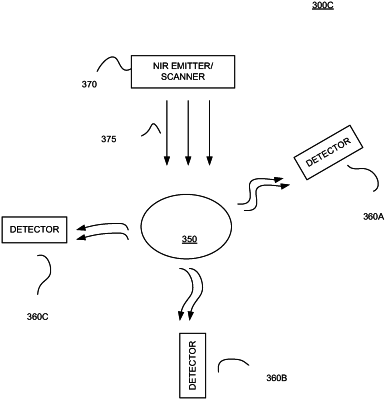
performing an in-treatment non-invasive optical scan on a region of a patient wherein said performing an optical scan comprises transmitting a near infrared (NIR) beam, from an NIR energy source that is positioned outside said patient, into and through tissue of said patient;
detecting signals from said optical scan,
wherein said detecting includes detecting reflected NIR energy reflected off the patient, detecting transmitted NIR energy transmitted through the patient, and detecting emitted NIR energy emitted from the patient,
wherein said signals from said optical scan include a first plurality of detected signals, and wherein said first plurality of detected signals include i) contributions of skin characteristics, and ii) signals produced by scattering and reflectance, of said NIR beam from said NIR energy source, by a skeletal anatomy of said patient associated with said region;
filtering out said contributions of skin characteristics from said first plurality of detected signals, to produce a second plurality of detected signals; and
determining said skeletal anatomy associated with said region from said second plurality of detected signals.
|
|
8. A system, comprising:
a skin detector for determining skin characteristics in a region inside a patient;
a first in-treatment NIR energy source;
a first nearinfrared (NIR) optical scanner configured to perform a first optica; scan on said region of said patient, said first optical scan including varying frequencies and intensities of said first in-treatment NIR energy source;
a frequemcy and intensity selector configured to determine a frequency and intensity combination to illuminate a skeletal anatomy associated with said region with minimal skin signaling characteristics based on the first optical scan;
a second in-treatment NIR energy source outside of said patient;
a second NIR optical scanner for performing a second optical scan on said region of said patient, said second optical scan including transmission of an NIR beam from said second in-treatment NIR energy source from outside said patient and into and through tissue of said patient, said NIR beam being based on said frequency and intensity combination;
at least one detector configured to detect signals from said second optical scan, wherein said signals from said second optical scan include a first plurality of detected signals, and wherein said first plurality of detected signals include i) contributions of skin characteristics, and ii) signals produced by scattering and reflectance, of said NIR beam from said second in-treatment NIR energy source, by said. skeletal anatomy of said patient associated with said region;
a filter for filtering out said contributions of skin characteristics from said first plurality of detected signals, to produce a second plurality of detected signals; and
a modeling module for determining said skeletal anatomy associated with said region from said second plurality of detected signals.
|