| CPC H01L 24/29 (2013.01) [B23K 35/262 (2013.01); B23K 35/302 (2013.01); C22C 13/00 (2013.01); H01L 24/83 (2013.01); B23K 2101/42 (2018.08); H01L 2224/29209 (2013.01); H01L 2224/29211 (2013.01); H01L 2224/29216 (2013.01); H01L 2224/29239 (2013.01); H01L 2224/29247 (2013.01); H01L 2224/29311 (2013.01); H01L 2224/29324 (2013.01); H01L 2224/29339 (2013.01); H01L 2224/29347 (2013.01); H01L 2224/29355 (2013.01); H01L 2224/29364 (2013.01); H01L 2224/29369 (2013.01); H01L 2224/83815 (2013.01); H01L 2924/014 (2013.01); H01L 2924/0105 (2013.01); H01L 2924/01013 (2013.01); H01L 2924/01028 (2013.01); H01L 2924/01029 (2013.01); H01L 2924/01046 (2013.01); H01L 2924/01047 (2013.01); H01L 2924/01049 (2013.01); H01L 2924/01078 (2013.01); H01L 2924/01082 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
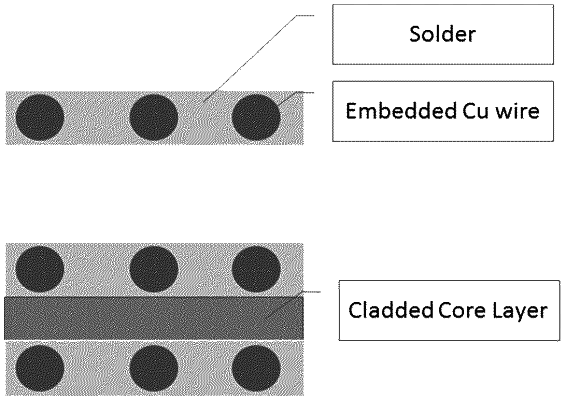
1. A solder material comprising:
a) a solder alloy, and
b) a thermal conductivity modifying component,
wherein the solder alloy is selected from the group consisting of high lead alloys, SnAg alloys, SnAgCu alloys, SnPb alloys, and combinations of one or more of the foregoing;
wherein the thermal conductivity modifying component is in the form of a wire;
wherein the thermal conductivity modifying component is tin over nickel over aluminum; and
wherein the solder material has a bulk thermal conductivity of between about 75 and about 150 W/m-K.
|