| CPC G06V 10/774 (2022.01) [G06F 11/261 (2013.01); G06F 11/3684 (2013.01); G06F 18/217 (2023.01); G06F 30/20 (2020.01); G06F 18/214 (2023.01); G06F 30/27 (2020.01); G06F 2111/18 (2020.01); G06T 7/70 (2017.01); G06T 19/003 (2013.01); G06T 19/006 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
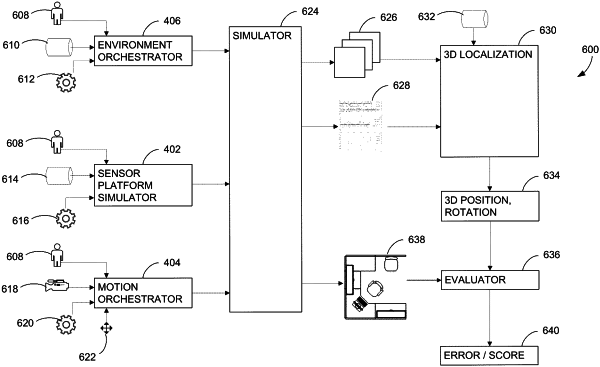
1. A method comprising:
simulating a virtual environment;
varying lighting in different instances of the simulated virtual environment for testing a localization algorithm;
simulating three-dimensional (3D) motion of a first hardware configuration within the different instances of the virtual environment in which the lighting is varied;
generating synthetic experiment data for the first hardware configuration having the simulated 3D motion within the virtual environment in which the lighting is varied;
applying the localization algorithm to the first hardware configurations with the simulated 3D motion in the virtual environment in which the lighting is varied;
determining disparity data of the localization algorithm against ground truth data from the localization algorithm applied to the simulated first hardware configuration with the simulated 3D motion in the virtual environment in which the lighting is varied;
determining that the disparity data exceeds a variance threshold;
directing an artificial intelligence (AI) application to run subsequent testing of the localization algorithm against a second hardware configuration different from the first hardware configuration; and
modifying the localization algorithm based on the subsequent testing.
|