| CPC G01S 17/931 (2020.01) [G01S 7/4808 (2013.01); G01S 17/08 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A vehicle comprising:
a time-of-flight sensor configured to generate data based on light received at a receiver of the time-of-flight sensor;
one or more processors; and
memory storing processor-executable instructions that, when executed by the one or more processors, configure the vehicle to perform acts comprising:
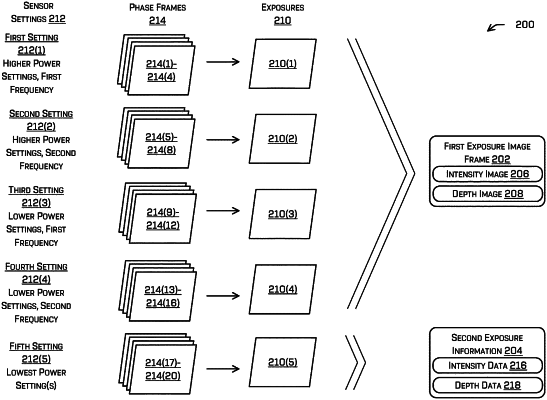
receiving, from the time-of-flight sensor, first sensor data comprising a plurality of first phase frames, the first phase frames comprising first phase values for pixels of the receiver, and the first sensor data being associated with a first exposure time;
receiving, from the time-of-flight sensor, second sensor data comprising a plurality of second phase frames, the second phase frames comprising second phase values for the pixels of the receiver, and the second sensor data being associated with a second exposure time shorter than the first exposure time;
determining first intensity information from the first phase values and second intensity information from the second phase values;
determining, based at least in part on the first intensity information and the second intensity information, a saturation value associated with the first exposure and the second exposure;
generating, based on the saturation value, a signal to alter one or more of the first exposure time or the second exposure time associated with the time-of-flight sensor; and
sending the signal to the time-of-flight sensor;
wherein the saturation value is based at least in part on a number of unreliable pixels.
|