| CPC C08G 63/672 (2013.01) | 4 Claims |
|
1. A method for producing a polyester resin comprising:
a diol constituent unit comprising a unit a1 derived from spiroglycol represented by formula (1) and a unit a2 derived from ethylene glycol; and
a dicarboxylic acid constituent unit comprising a unit b derived from terephthalic acid and/or an ester thereof,
wherein
a content of the unit a1 is from 5 to 60 mol % and a content of the unit a2 is from 30 to 95 mol %, based on a total amount of the unit a1 and the unit a2,
a content of the unit b is from 80 to 100 mol % based on a total amount of the dicarboxylic acid constituent unit, and
the following conditions (1) to (3) are satisfied:
(1) an intrinsic viscosity V1 of the polyester resin is from 0.45 to 0.85 dL/g, the intrinsic viscosity V1 being measured at 25° C. by using a mixed solvent comprising phenol and 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane in a weight ratio of 6:4;
(2) when an operation of extruding the polyester resin at a shear rate of 122 (l/s) is performed after the polyester resin is kept at 240° C. for 5 minutes, a reduction percentage of intrinsic viscosities before and after the operation, in terms of (V1-V2)/V1, is 3% or less, where V2 refers to an intrinsic viscosity measured based on the condition (1) after the operation; and
(3) a glass transition temperature of the polyester resin measured by a differential scanning calorimeter is 90° C. or higher and a heat quantity of a crystallization exothermic peak during temperature decrease is 5 J/g or less,
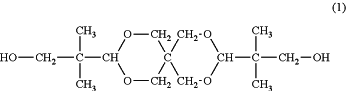 , the method comprising:
subjecting the ethylene glycol and the terephthalic acid and/or an ester thereof to an esterification reaction to thereby produce a precursor ester; and
adding the spiroglycol to the precursor ester,
wherein, in the adding, stirring is performed under a condition expressed by expressions (A) and (B) by using a stirrer equipped with a stirring blade:
7011×log (spiroglycol addition rate (kg/hr))+1.339+0.5≥stirring blade tip speed (m/s)≥0.7011×log (spiroglycol addition rate (kg/hr))+1.339−0.5 expression (A)
5≤stirring blade tip speed (m/s) expression (B).
|