| CPC C07C 235/80 (2013.01) [A61P 21/00 (2018.01); A61P 25/00 (2018.01); A61P 25/16 (2018.01); A61P 27/00 (2018.01); C07C 235/32 (2013.01); C07C 235/78 (2013.01); C07C 317/28 (2013.01); C07D 207/26 (2013.01); C07D 207/27 (2013.01); C07D 211/46 (2013.01); C07D 213/40 (2013.01); C07D 213/51 (2013.01); C07D 233/61 (2013.01); C07D 265/30 (2013.01); C07D 295/116 (2013.01); C07D 295/13 (2013.01); C07D 295/185 (2013.01); C07D 295/192 (2013.01); C07D 311/66 (2013.01); C07C 2601/02 (2017.05); C07C 2601/16 (2017.05)] | 13 Claims |
|
1. A method of treating a mitochondrial disorder, the method comprising contacting mitochondria in a cell of a subject with a therapeutically effective amount or effective amount of one or more compounds selected from Formula I:
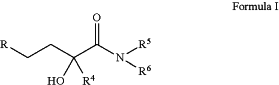 where R is selected from the group consisting of
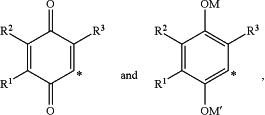 where the * indicates the point of attachment of R to the remainder of the molecule;
R1, R2, and R3 are independently selected from hydrogen and C1-C6-alkyl;
R4 is C1-C6-alkyl;
R5 is hydrogen;
R6 is selected from hydroxy, alkoxy, C1-C40-alkyl, C2-C40-alkenyl, C2-C40-alkynyl, and aryl;
where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, and aryl groups are optionally substituted with —OR10, —S(O)0-2R10, —CN, —F, —Cl, —Br, —I, —NR10R10′, oxo, C3-C6-cycloalkyl, aryl, aryl-C1-C6-alkyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, —C(O)—R11, —C(O)—C0-C6-alkyl-aryl, —C(O)—O—R11, —C(O)—O—C0-C6-alkyl-aryl, —C(O)—NR11R11, —C(O)—NH—C0-C6-alkyl-aryl, —NH—C(O)—R11, —NH—C(O)—C0-C6-alkyl-aryl; where the aryl, heteroaryl and heterocyclyl ring substituents may be further substituted with C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-haloalkyl, oxo, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, —C(O)—C1-C6-alkyl and —C(O)—O—C1-C6-alkyl; and where one of the carbons of the alkyl, alkenyl, or alkynyl groups may be substituted with a heteroatom selected from —O—, —N— or —S—; or
R5 and R6 together with the atom to which they are attached form a saturated or unsaturated 3-8 membered ring, optionally incorporating 1, 2, or 3 additional N, O, or S atoms, optionally substituted with oxo, —OR10, —SR10, —CN, —F, —Cl, —Br, —I, —NR10R10′, C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-haloalkyl; hydroxy-C1-C6-alkyl, —C(O)—H, —C(O)—C1-C6-alkyl, —C(O)-aryl, —C(O)—OH, or —C(O)—O—C1-C6-alkyl; or
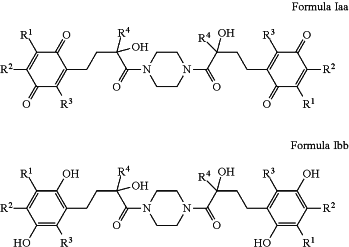
R5 and R6 together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached form a N,N′-disubstituted piperazine where the nitrogen substitution at the 4-position is a group identical to the substitution at the 1-position forming a compound of formula Iaa or Ibb, where R1, R2, R3, and R4 are as defined above:
 R10 and R10′ are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-haloalkyl, aryl, aryl-C1-C6-alkyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, —C(O)—H, —C(O)—C1-C6-alkyl, —C(O)-aryl and —C(O)—C1-C6-alkyl-aryl;
R11 and R11′ are selected from hydrogen and C1-C6-alkyl; and
M and M′ are independently selected from hydrogen, —C(O)—R12, —C(O)—C1-C6-alkenyl, —C(O)—C1-C6-alkynyl, —C(O)-aryl; —C(O)-heteroaryl, —C(O)O—R12, —C(O)NR12R12, —SO2OR12, —SO2—C1-C6-alkyl, —SO2-haloC1-C6-alkyl; —SO2-aryl, —SO2—NR12R12, —P(O)(OR12)(OR12), and C-linked mono or di-peptide, where R12 is hydrogen or C1-C6-alkyl optionally substituted with —OH, —NH2, —NH(C1-C4alkyl), —N(C1-C4alkyl)2, —C(O)—OH, —C(O)—O—C1-C4-alkyl or halogen;
and a salt, a stereoisomer, and a mixture of stereoisomers thereof;
wherein the mitochondrial disorder is selected from the group consisting of Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON); Kearns-Sayre Syndrome (KSS); Friedreich's Ataxia (FA) Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's Disease.
|