| CPC B60W 60/0016 (2020.02) [B60W 30/09 (2013.01); B60W 30/0953 (2013.01); B60W 30/0956 (2013.01); B60W 30/181 (2013.01); B60W 30/18163 (2013.01); B60W 40/02 (2013.01); B60W 40/105 (2013.01); B60W 40/107 (2013.01); B60W 60/0015 (2020.02); G05D 1/0214 (2013.01); G05D 1/0231 (2013.01); G05D 1/0246 (2013.01); G06T 7/20 (2013.01); G06T 7/70 (2017.01); G06V 20/58 (2022.01); G06V 20/584 (2022.01); G06V 40/10 (2022.01); B60W 2420/42 (2013.01); B60W 2420/52 (2013.01); B60W 2510/18 (2013.01); B60W 2520/105 (2013.01); B60W 2520/12 (2013.01); B60W 2520/125 (2013.01); B60W 2520/14 (2013.01); B60W 2530/201 (2020.02); B60W 2552/45 (2020.02); B60W 2554/4029 (2020.02); B60W 2554/4041 (2020.02); B60W 2554/4042 (2020.02); B60W 2554/4043 (2020.02); B60W 2554/4044 (2020.02); B60W 2554/80 (2020.02); B60W 2554/801 (2020.02); B60W 2555/60 (2020.02); B60W 2720/10 (2013.01); G05D 2201/0213 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30196 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30261 (2013.01); G06V 2201/07 (2022.01)] | 18 Claims |
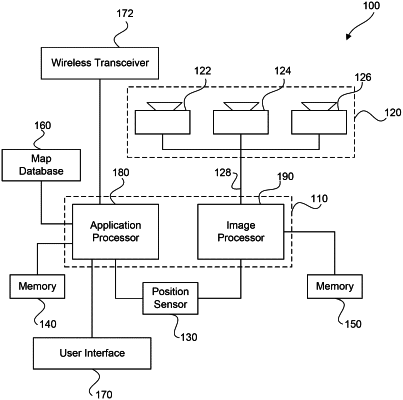
|
1. An automated driving system for a host vehicle, the system comprising:
an interface to obtain sensing data of an environment in a vicinity of the host vehicle, the sensing data captured from at least one sensor device of the host vehicle; and
at least one processing device configured to:
determine a planned navigational action for accomplishing a navigational goal of the host vehicle;
identify, from the sensing data, a target vehicle in the environment of the host vehicle;
predict a distance between the host vehicle and the target vehicle that would result if the planned navigational action was taken;
identify a braking rate of the host vehicle, a maximum acceleration capability of the host vehicle, a current longitudinal speed of the host vehicle, and a response time of the host vehicle to apply the braking rate;
determine a host vehicle stopping distance to bring the host vehicle to a stop, based on an evaluation of: (i) the identified braking rate of the host vehicle, (ii) the maximum acceleration capability of the host vehicle, (iii) the current longitudinal speed of the host vehicle, and (iv) the response time of the host vehicle to apply the identified braking rate, wherein the identified braking rate of the host vehicle is a submaximal braking rate that is less than a maximum braking capability of the host vehicle;
identify a braking rate of the target vehicle and a current longitudinal speed of the target vehicle;
determine a target vehicle stopping distance to bring the target vehicle to a stop, based on an evaluation of: (i) the identified braking rate of the target vehicle and (ii) the current longitudinal speed of the target vehicle; and
cause the host vehicle to continue with the planned navigational action while the predicted distance of the planned navigational action is greater than a minimum safe longitudinal distance, wherein the minimum safe longitudinal distance is calculated based on: (i) the host vehicle stopping distance, (ii) the target vehicle stopping distance, and (iii) an acceleration distance that corresponds to a distance the host vehicle is capable to travel during the response time at the maximum acceleration capability of the host vehicle, starting from the current longitudinal speed of the host vehicle.
|