| CPC B60G 3/26 (2013.01) [B60G 2200/18 (2013.01); B60G 2200/46 (2013.01); B60G 2200/462 (2013.01); B60G 2400/64 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
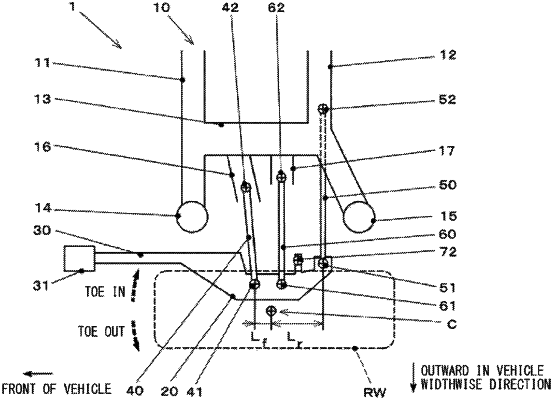
1. A suspension comprising:
a housing to which a hub bearing is attached, the hub bearing rotatably supporting a rear wheel of a vehicle;
a radius arm unitized with the housing and protruding from the housing toward front of the vehicle;
a radius arm bush disposed on a front end of the radius arm, the radius arm bush coupling the radius arm to a vehicle body of the vehicle, with an elastic body in between; and
a shock absorber configured to generate a damping force in response to vertical motion of the housing with respect to the vehicle body,
wherein an inclination angle θ1 and an inclination angle θ2 are set to satisfy the following expression (1)
ΔF·tan θ2>M·tan θ1 (1),
in which:
θ1 is an inclination angle at which a straight line coupling a center of the radius arm bush to a center of the rear wheel is inclined to a horizontal line, to lower toward the rear wheel, as viewed from a side of the vehicle in a steady state of the vehicle,
θ2 is an inclination angle at which an axis of expansion and shrink of the shock absorber is inclined to a vertical direction, to allow an upper end of the shock absorber to more forward from a lower end of the shock absorber,
M is an unsprung mass of the suspension, and
ΔF is an amount of increase in a vertical load on the rear wheel from the steady state during a shrinkwise stroke of the shock absorber.
|