| CPC B29C 39/003 (2013.01) [B29C 39/26 (2013.01); B29C 39/36 (2013.01); B29C 39/38 (2013.01); B29K 2023/065 (2013.01); B29K 2023/0625 (2013.01); B29K 2023/0633 (2013.01); B29K 2023/12 (2013.01); B29K 2023/16 (2013.01); B29K 2025/06 (2013.01); B29K 2027/06 (2013.01); B29K 2029/14 (2013.01); B29K 2033/12 (2013.01); B29K 2055/02 (2013.01); B29K 2067/003 (2013.01); B29K 2075/00 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
1. A method of fabricating and mass-producing a three-dimensional hierarchical structure, the method comprising:
a first phase comprising:
using a three-dimensional hierarchical structure as a master structure;
enclosing the master structure in an elastomer mold, wherein a Young's modulus of the elastomer mold is at least one order of magnitude lower than a Young's modulus of the master structure;
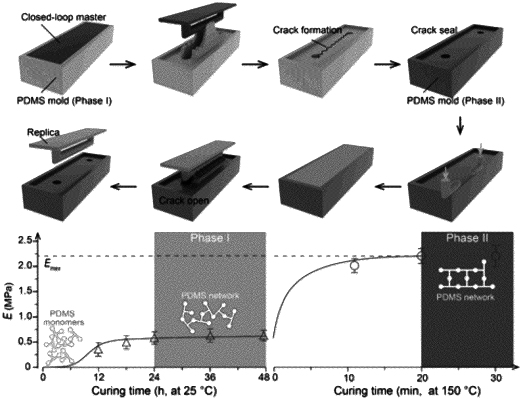
removing the master structure from the elastomer mold, wherein one or more controlled cracks are formed in the elastomer mold along the direction of a vertical peeling force, and a cavity mold is formed with a shape of the master structure in the elastomer mold; and
controlling the formation of the one or more controlled cracks in the elastomer mold by adjusting a curing temperature and a curing time of the elastomer mold, so that the one or more controlled cracks are formed at a locked region in the elastomer mold during the master structure removal, wherein the elastomer mold has a cracking coefficient η of at least 100% for preventing a neck region of the elastomer mold from breaking and a deformation coefficient φ during the first phase, wherein 1/φ is equal to or greater than the ultimate elongation at break of the elastomer mold so as to ensure that the elastomer mold is able to be separated from the master structure;
wherein the cracking coefficient is computed by:
η=Wmin/h,
wherein Wmin is the smallest width of the neck region;
h is the height of the locked region, and 2 μm<h<15 μm;
wherein the deformation coefficient is computed by:
φ=Wmin/Wmax,
wherein Wmin is the smallest width of the neck region;
Wmax is the largest width near the locked region;
a second phase comprising:
curing the elastomer mold at a temperature higher than the curing temperature during the first phase to enhance the stiffness, self-sealing and configurability of the elastomer mold;
filling the cavity mold with a replica material and curing the replica material to fabricate a replica of the master structure; and
removing the replica from the elastomer mold.
|