| CPC G21D 3/001 (2013.01) [G21C 17/112 (2013.01); G21D 3/04 (2013.01); G21D 3/005 (2019.01); Y02E 30/30 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
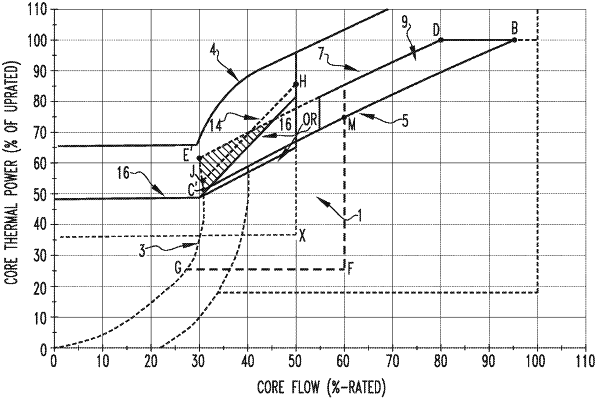
1. A method for protecting a nuclear reactor core from fuel damage due to thermal hydraulic instability in an extended operating domain for an extended power uprate, comprising:
generating a power-flow operating map, comprising:
establishing a natural circulation curve;
establishing a Maximum Extended Load Line Limit Analysis (MELLLA) control rod line; and
establishing a higher MELLLA+ control rod line positioned above the MELLLA control rod line;
forming a MELLLA+ domain above the MELLLA control rod line, up to the higher MELLLA+ control rod line;
identifying a predetermined core flow rate;
calculating by a thermal hydraulic code simulator a thermal hydraulic stability limit for core flow rates less than or equal to the predetermined core flow rate;
determining a power level that corresponds to the thermal hydraulic stability limit at different core flow rates that are less than or equal to the predetermined core flow rate;
providing an Average Power Range Monitor (APRM) flow-biased scram line;
lowering the APRM flow-biased scram line to below the thermal hydraulic stability limit based on the core flow rate being less than or equal to the predetermined core flow rate; and
when operating in the MELLLA+ domain, actuating an APRM-based trip system based on a core flow decrease resulting from a flow decrease transient and power increases above the power level to provide an automatic anticipatory scram or a selected rod insertion trip to cause a power reduction.
|