| CPC G06F 3/016 (2013.01) [G01D 5/14 (2013.01); G01D 5/16 (2013.01); G01D 5/20 (2013.01); G01D 5/24 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
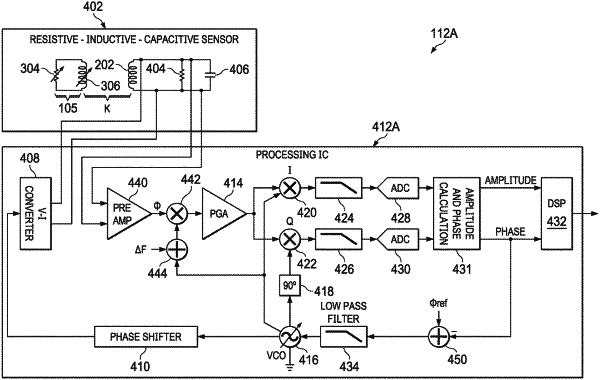
|
1. A system comprising:
at least one resistive-inductive-capacitive sensor in electrical communication with a human-machine interface such that human interaction with the human-machine interface causes a displacement in a mechanical member of the human-machine interface which in turn causes variance in an impedance of the at least one resistive-inductive-capacitive sensor; and
a control circuit configured to:
maintain timing parameters for operation of the at least one resistive-inductive-capacitive sensor; and
vary at least one of the timing parameters to control a spectrum associated with the at least one resistive-inductive-capacitive sensor, wherein the spectrum comprises one of a sensor activity spectrum of the at least one resistive-inductive-capacitive sensor and a current usage spectrum associated with electrical current delivered to the at least one resistive-inductive-capacitive sensor from a source of electrical energy.
|