| CPC C11D 7/04 (2013.01) [C02F 1/42 (2013.01); C02F 1/685 (2013.01); C11D 7/50 (2013.01); C11D 11/0047 (2013.01); B08B 3/08 (2013.01); C02F 2001/422 (2013.01); C02F 2001/425 (2013.01); C02F 2103/04 (2013.01); C02F 2103/346 (2013.01)] | 1 Claim |
|
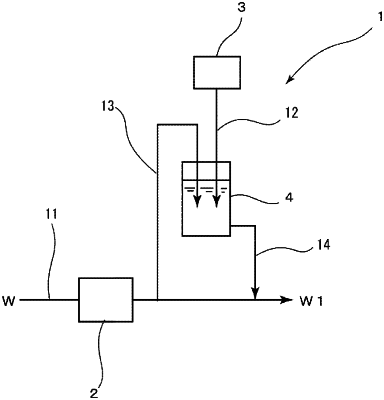
1. A conductive aqueous solution production device comprising:
a main pipe;
an ion exchange device provided in the main pipe and configured to circulate raw water;
a branch pipe that branches from the main pipe at a branch point downstream of the ion exchange device;
a supply pipe that merges into the main pipe at a junction point downstream of the ion exchange device and downstream of the branch point;
a preliminary dilution storage tank that communicates with the branch pipe and the supply pipe and for being supplied with a part of a treated water which has passed through the ion exchange device; and
a conductivity-imparting substance supply device configured to add a conductivity-imparting substance to the treated water in the preliminary dilution storage tank,
wherein the conductivity-imparting substance is ammonia,
wherein ions, which are generated by dissolving the ammonia in the part of the treated water and impart conductivity to the part of the treated water, are cations,
wherein the ion exchange device is filled with a cation exchanger,
wherein a separation distance between an outlet of the ion exchange device and the junction point in the main pipe is 5 m or less,
wherein the raw water to be supplied to the ion exchange device is pure water or ultrapure water having a metal ion concentration of 10 ng/L or less, and
wherein the metal ion concentration in a conductive aqueous solution that flows through the main pipe downstream of the junction point is 1 ng/L or less.
|