| CPC C10G 2/30 (2013.01) [C01B 3/40 (2013.01); C10J 3/00 (2013.01); C10K 1/004 (2013.01); C10K 1/005 (2013.01); C01B 2203/0233 (2013.01); C01B 2203/0244 (2013.01); C01B 2203/061 (2013.01); C01B 2203/062 (2013.01); C01B 2203/068 (2013.01); C01B 2203/1058 (2013.01); C01B 2203/1223 (2013.01); C01B 2203/1229 (2013.01); C01B 2203/1241 (2013.01); C10G 2400/04 (2013.01); C10G 2400/08 (2013.01); C10J 2300/092 (2013.01); C10J 2300/0946 (2013.01); C10J 2300/1618 (2013.01); C10J 2300/1659 (2013.01); C10J 2300/1665 (2013.01); C10J 2300/1668 (2013.01); C10J 2300/1846 (2013.01)] | 25 Claims |
|
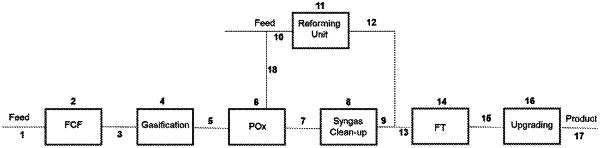
1. A process for the manufacture of a useful product from synthesis gas having a desired hydrogen to carbon monoxide molar ratio comprising:
gasifying a first carbonaceous feedstock comprising waste materials and/or biomass in a gasification zone to produce a first synthesis gas;
partially oxidising the first synthesis gas in a partial oxidation zone to generate oxidised synthesis gas;
reforming a second carbonaceous feedstock comprising renewable natural gas to produce a second synthesis gas, in which reforming the carbon monoxide content and the hydrogen content are both increased, the second synthesis gas having a different hydrogen to carbon monoxide ratio from that of the first synthesis gas;
combining at least a portion of the first partially oxidised synthesis gas and at least a portion of the second synthesis gas in an amount to achieve the desired hydrogen to carbon monoxide molar ratio and to generate a combined synthesis gas;
subjecting at least part of the combined synthesis gas to a conversion or separation process effective to produce the useful product.
|