| CPC B29C 64/165 (2017.08) [B29C 64/264 (2017.08); B33Y 10/00 (2014.12); B33Y 30/00 (2014.12); B33Y 70/00 (2014.12); B29K 2105/005 (2013.01); B29K 2309/08 (2013.01); B29K 2995/0046 (2013.01); B29K 2995/0063 (2013.01); B29K 2995/0077 (2013.01); B29K 2995/0097 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
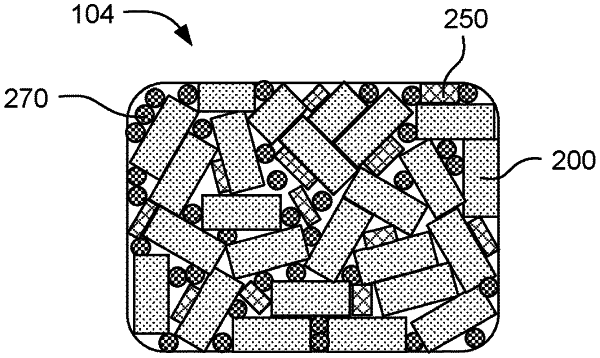
1. A materials kit for 3D printing comprising:
a powder bed material including from about 60 wt % to 100 wt % composite fibers having an average aspect ratio from about 3:1 to about 30:1, the composite fibers including glass fibers at from about 5 wt % to about 40 wt % based on the total weight of the powder bed material, wherein the glass fibers include at least one of glass fibers coated with an encapsulating polymer, uncoated glass fibers, or a combination thereof; and
a fusing agent comprising an energy absorber to absorb electromagnetic radiation to produce heat.
|