| CPC A61B 5/1102 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0002 (2013.01); A61B 5/7207 (2013.01); A61B 5/7264 (2013.01)] | 24 Claims |
|
1. A method to remove motion-associated artifacts from an acquired measurement signal, wherein the acquired measurement signal is used to non-invasively assess a cardiac disease state or abnormal cardiac condition of a subject, the method comprising:
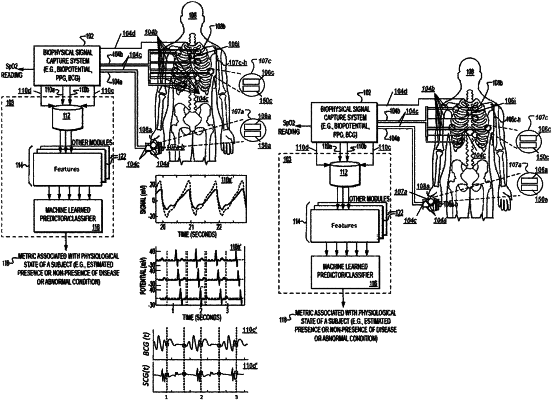
obtaining, by one or more processors, a first biophysical signal data set of the subject comprising a first photoplethysmographic signal and a second photoplethysmographic signal-or a cardiac signal;
obtaining, by the one or more processors, a second biophysical signal data set of the subject associated with a ballistocardiogram signal, wherein the ballistocardiogram signal are temporally and spatially acquired with respect to the first photoplethysmographic signal, the second photoplethysmographic signal, or the cardiac signal;
determining, by the one or more processors, a filtered biophysical-signal data set of the first biophysical signal data set by removing an estimated motion signal determined using the ballistocardiogram signal;
determining, by the one or more processors, one or more dynamical features including a first dynamical feature and a second dynamical feature, wherein the first and second dynamical features each characterize, via a statistical-or dynamical-analysis assessment, one or more dynamical properties across multiple heart cycles of the second biophysical signal data set associated with the ballistocardiogram signal;
determining, by the one or more processors, via a trained classifier model and based, at least in part on the determined one or more dynamical features, an estimated value related to a presence or non-presence of the cardiac disease state or abnormal condition; and
in response to determining the presence of the cardiac disease state or abnormal condition, outputting, by the one or more processors and via a report and/or display, a recommended treatment for the cardiac disease state or abnormal condition, wherein the treatment is selected based on the estimated value determined via the trained classifier model.
|