| CPC H04Q 11/0067 (2013.01) [H04B 10/27 (2013.01); H04Q 2011/0088 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
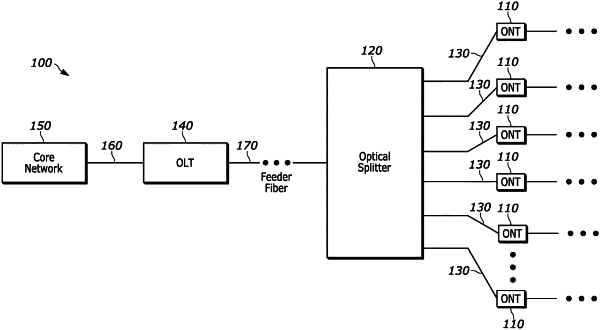
1. An optical network terminal including a processor comprising:
(a) said optical line terminal capable of receiving digital data from a core network from a first connection and provide optical digital data representative of said digital data from said core network to an optical network terminal though an optical fiber connection associated with said optical line terminal;
(b) said optical line terminal capable of receiving optical digital data from said optical network terminal through said optical fiber connection associated with said optical line terminal and provide digital data representative of said optical digital data from said optical network terminal to a core network;
(c) said optical digital data from said optical network terminal including chirp, wherein said chirp includes temporary wavelength changes of a signal representative of said optical digital data as a result of changes in logic levels of said signal, wherein said logic levels are based upon a non-return to zero modulation;
(d) said optical line terminal processing said signal representative of said optical digital data from said optical network terminal in a manner determines changes in said logic levels based upon said temporary wavelength changes of said signal.
|