| CPC H02J 7/1423 (2013.01) [H02J 7/0063 (2013.01); H02M 1/0043 (2021.05); H02P 25/022 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
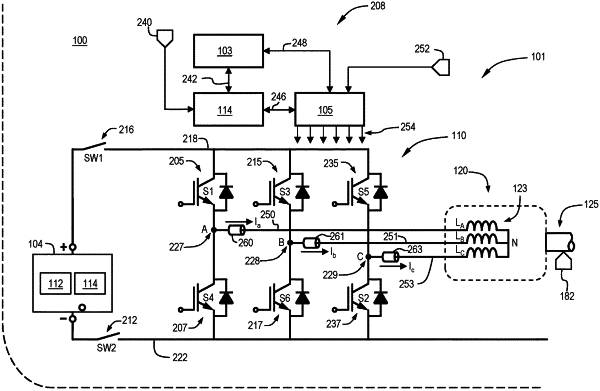
4. An apparatus for shuttling charge between a pair of batteries, comprising:
the pair of batteries configured in series;
a motor including a stator winding having a plurality of stator phase windings commonly coupled at a neutral terminal and having respective phase terminals;
a power inverter having a plurality of phase legs coupled between positive and negative DC rails, the positive and negative DC rails coupled across the pair of batteries configured in series, and each phase leg including respective upper and lower solid-state switches with a respective phase pole therebetween coupled to a respective one of the stator phase windings at its corresponding phase terminal;
a switch between a midpoint node of the pair batteries configured in series and the stator winding, wherein the switch between the midpoint node of the pair of batteries configured in series and the stator winding comprises a switch between the midpoint node of the pair of batteries configured in series and the respective phase terminal of one of the stator phase windings; and
a controller:
operating the switch closed to couple the midpoint node of the pair of batteries configured in series to at least one phase winding of the plurality of stator phase windings; and
controlling conduction of the phase legs of the power inverter to operate the power inverter and the stator winding as a switched-mode power converter comprising at least one of the stator phase windings and one of the upper and lower solid-state switches of at least one of the phase legs,
wherein controlling conduction of the phase legs of the power inverter to operate the power inverter and the stator winding as a switched-mode power converter comprises interleaved pulse width modulation control of the power inverter.
|