| CPC G05D 23/1904 (2013.01) [G05D 23/1923 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
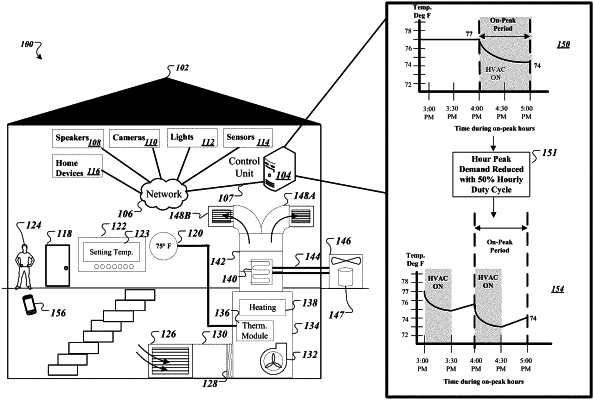
maintaining first data that identifies a predicted on-peak time period for a monitored property that corresponds to predicted energy usage at the monitored property, wherein the predicted on-peak time period is based on information received from a utility company;
maintaining second data indicative of a requested temperature for the monitored property at a time during the time period;
determining that a temperature difference between the requested temperature and a current temperature of the monitored property does not satisfy a threshold value;
in response to determining that the temperature difference does not satisfy the threshold value, determining a predicted amount of time required by a Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) system of the monitored property to adjust from the current temperature to a second temperature, the second temperature being a temperature such that a difference between the requested temperature and the second temperature satisfies the threshold value;
determining whether a time difference between a current time to a start of the time period satisfies the predicted amount of time; and
prior to the start of the time period and in response to determining the time difference satisfies the predicted amount of time, instructing the HVAC system of the monitored property to execute a pre-cooling or a pre-heating process, wherein the pre-cooling or the pre-heating processes causes a temperature at the monitored property to satisfy the second temperature before the time period.
|