| CPC G05B 23/0283 (2013.01) [G05B 23/0208 (2013.01); G05B 23/0254 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. A method, comprising:
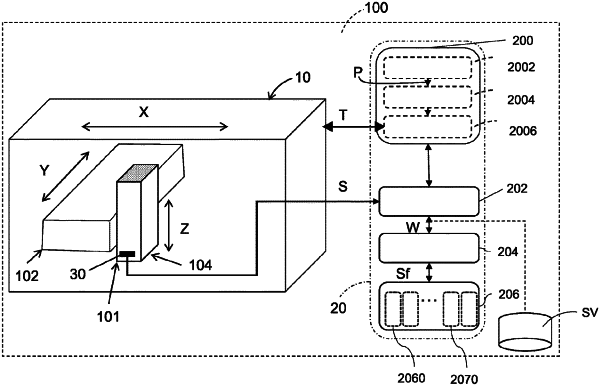
performing diagnosis of operation of a machine tool comprising at least one sensor coupled to said machine tool, wherein the machine tool comprises an end-effector configured to be moved along one or more axes of a working envelope by one or more actuators,
said method comprising operations of:
generating a programming sequence of movement of the end-effector along one or more axes of said machine tool, wherein the programming sequence comprises machining-programming sequence instructions to apply at least one single impulsive variation of a kinematic quantity of movement of the end effector along one or more axes;
controlling the movement of the end-effector along one or more axes of said machine tool by means of a control chain comprising:
performing said operation of generating said programming sequence, obtaining as a result a trajectory of movement for actuation of one or more axes of said machine tool from said programming sequence, and
supplying said trajectory of movement for actuation of one or more axes of said machine tool to actuators of said one or more axes;
receiving a read-out signal of said at least one sensor coupled to said machine tool; and
processing said read-out signal of said at least one sensor coupled to said machine tool,
generating a reference read-out signal corresponding to the machining-programming sequence without the at least one single impulsive variation;
comparing said read-out signal with the reference read-out signal; and
modifying the read-out signal based on the comparison;
wherein said impulsive variation is included in a machining-programming sequence predetermined on the basis of a workpiece to be machined within the working envelope of the machine tool,
said machining-programming sequence comprising instructions that apply at least one single impulsive variation of a kinematic quantity of movement of the end-effector with respect to one or more actuators in said trajectory of movement, so that the at least one single impulsive variation-propagates through said control chain,
wherein said operation of processing said read-out signal comprises processing a response of said machine tool to said at least one single impulsive variation included in the machining-programming sequence, and wherein said operation of processing said read-out signal comprises an artificial-neural-network processing via one or more artificial neural networks configured for analysing one or more signals indicative of the status of the machine tool in said read-out signal.
|