| CPC A61N 1/36146 (2013.01) [A61N 1/36025 (2013.01); A61N 1/36071 (2013.01); A61N 1/36139 (2013.01); A61N 1/37247 (2013.01); A61N 1/37264 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method for programming a neuromodulator with a selected neuromodulation parameter set, the method comprising:
programming the neuromodulator with a schedule of different neuromodulation parameter sets to deliver sub-perception neuromodulation to a patient;
delivering sub-perception neuromodulation to a patient with the neuromodulator, using each of the different neuromodulation parameter sets in the schedule;
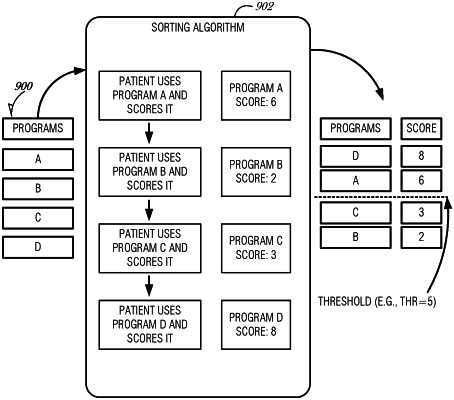
accessing, using a computerized system, a feedback input indicative of neuromodulation efficacy for each of the different neuromodulation parameter sets in the schedule;
ranking, using the computerized system and the feedback input, the neuromodulation efficacy for each of the different neuromodulation parameter sets in the schedule to provide evaluation results for the different neuromodulation parameter sets;
determining, using a machine learning algorithm of the computerized system, a revised schedule of neuromodulation parameter sets based on the evaluation results from at least one previous schedule, wherein the revised schedule differs from an immediately preceding schedule by including at least one different parameter set than was included in the immediately preceding schedule;
programming, using the computerized system, the neuromodulator with the revised schedule of neuromodulation parameter sets;
delivering sub-perception neuromodulation to the patient with the neuromodulator, using each of the different neuromodulation parameters sets in the revised schedule; and
iterating the accessing, the ranking, the determining, and the programming with adaptive learning until the evaluation results indicate that the selected neuromodulation parameter set was used to deliver sub-perception neuromodulation.
|