| CPC A61B 5/14532 (2013.01) [A61B 5/7221 (2013.01); A61B 5/7267 (2013.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); A61B 5/742 (2013.01); A61B 5/7475 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06N 20/20 (2019.01); G16H 40/63 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
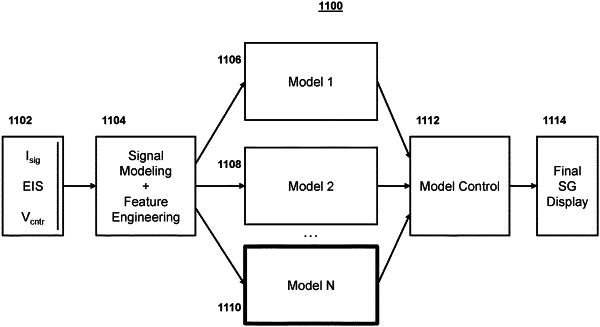
1. A sensor device for applying layered machine learning models to reduce sensor glucose signal blanking, the sensor device comprising:
memory configured to store a plurality of machine learning models, wherein each machine learning model of the plurality of machine learning models differs with respect to one or more data characteristics comprising probabilistic reliance and is trained using training data comprising clinical data on sensor glucose behavior; and
a processor configured to:
receive continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) sensor data comprising:
an interstitial current signal;
an electrochemical impedance spectroscopy signal;
a counter voltage; or
any combination thereof;
input the CGM sensor data into the plurality of machine learning models;
receive outputs from the plurality of machine learning models indicating a plurality of predicted sensor glucose values; and
generate for display, on a display interface, a sensor glucose value based on weighting the plurality of predicted sensor glucose values according to probabilistic reliance of each of the plurality of machine learning models.
|