| CPC A61B 3/1233 (2013.01) [A61B 3/102 (2013.01); A61B 5/489 (2013.01); A61B 5/4893 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
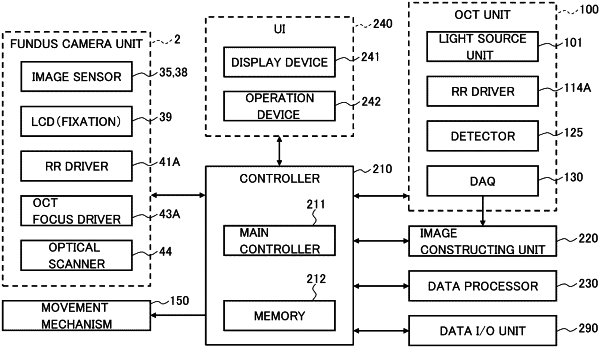
1. A blood flow measurement apparatus comprising:
a scanning optical system including an optical coherence tomography (OCT) scanner and configured to apply optical coherence tomography scanning to a fundus of a subject's eye;
a front image acquiring sensor or memory configured to acquire a front image of the fundus;
processing circuitry configured to determine a region of interest that intersects a blood vessel by analyzing the front image based on a condition set in advance;
the processing circuitry further configured to control the scanning optical system to apply a repetitive OCT scan to the region of interest; and
the processing circuitry further configured to acquire blood flow information based on data collected by the repetitive OCT scan,
wherein the processing circuitry is further configured to identify a blood vessel of interest by analyzing the front image based on a blood vessel identification condition set in advance, and the processing circuitry determines a region of interest that intersects the blood vessel of interest identified,
the front image includes an optic nerve head image,
the processing circuitry identifies, as the blood vessel of interest, a thickest blood vessel for each of two or more regions located in mutually different directions with respect to the optic nerve head image, the thickest blood vessel having a largest diameter in a corresponding region, and
the processing circuitry determines the region of interest that intersects any of two or more thickest blood vessels identified for the two or more regions.
|