| CPC H03G 3/3005 (2013.01) [H04R 3/00 (2013.01); H04R 19/04 (2013.01); H03G 2201/103 (2013.01); H04R 2201/003 (2013.01); H04R 2430/01 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
1. An apparatus, comprising:
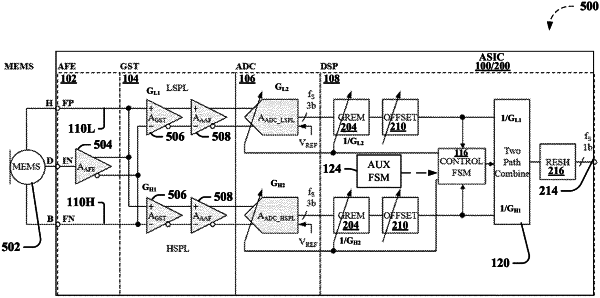
an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) associated with a microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) acoustic sensor and having a plurality of signal paths associated with the MEMS acoustic sensor, wherein the plurality of signal paths have different gains provided by a plurality of gain stage amplifiers;
a digital signal processing component (DSP) associated with the ASIC configured to receive a plurality of signals from a plurality of adjustable analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) associated with the plurality of gain stage amplifiers; and
a gain adjustment component associated with the DSP configured to adjust respective gains associated with the plurality of adjustable ADCs based at least in part on respective signal levels associated with the plurality of signal paths, wherein the gain adjustment component is further configured to coordinate switching among at least respective portions of the plurality of signal paths based at least in part on the respective signal levels and a selected transition of modes based at least in part on at least one of a performance criteria or a power consumption criteria, and wherein the gain adjustment component is further configured to coordinate temporary power reduction and power restoration associated with an unused portion of the plurality of signal paths based at least in part on the selected transition of modes and respective signal levels associated with the plurality of signal paths.
|