| CPC G01V 3/38 (2013.01) [G01V 3/12 (2013.01)] | 3 Claims |
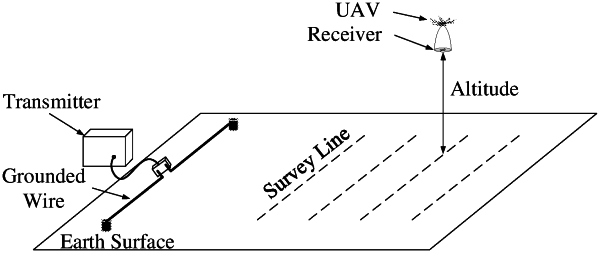
|
1. An estimation method of detecting elevation by a semi-airborne electromagnetic method, comprising
S1, judging original elevation data to obtain wrong point data and normal data;
wherein judging the original elevation data comprises:
judging the original elevation data according to orders of from a first to a last and from the last to the first of a survey line by using a judging index method based on a Mahalanobis distance, and respectively obtaining wrong point data sets Aforward and Ainverse;
wherein a judging index based on the Mahalanobis distance is:
yk=((yk−ŷk−)T(Pŷk−)−1)(yk−ŷk−))2=(yk−ŷk−)T(Pŷk−)−1(yk−ŷk−)
wherein yk is the judging index, yk is an actual measured value of the elevation, ŷk− is a predicted measured value of the elevation, and Pŷk− is a covariance of ŷk−;
fusing the wrong point data sets Aforard and Ainverse, taking an intersection of the two data sets as the wrong point data, and taking data except the wrong point data in the original elevation data as the normal data;
S2, filtering the wrong point data by an improved Kalman filtering method, and filtering the normal data by a conventional Kalman filtering method;
wherein the improved Kalman filtering method is:
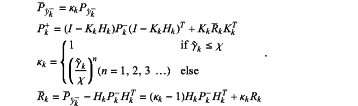 wherein Pŷk− is a covariance of an adjusted observation and prediction value, kk is an adjusting coefficient, Pk+ is a covariance of a posterior estimation value, Kk is a Kalman filtering coefficient, Hk is an observation matrix, Pk− is a covariance between a real value and a prediction value, Rk is a calculated auxiliary parameter of Pk+, KkT is a transposition of the Kalman filtering coefficient, yk is the judging index, χ is a preset threshold, HkT is a transposition of the observation matrix, and Rk is a covariance of an observation noise matrix;
S3, fusing a filtering result of the wrong point data and a filtering result of the normal data, and taking a fused result as a measured value sequence used in a next working process; and
S4, repeating the S1-S3 until the fused result meets preset requirements, and completing an effective estimation of a surface elevation.
|