| CPC G01N 15/1434 (2013.01) [G03H 1/0866 (2013.01); G01N 2015/1445 (2013.01); G01N 2015/145 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
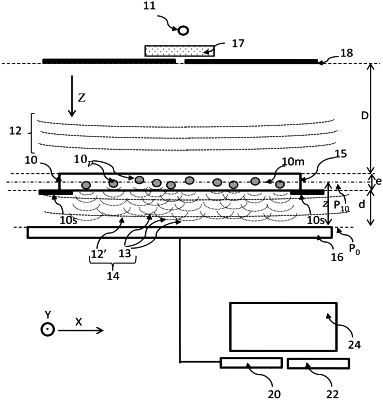
1. A method for characterizing a particle within a sample, the sample lying between an image sensor and a light source, the image sensor lying in a detection plane, the method comprising:
a) illuminating the sample with the light source, the light source emitting an incident light wave that propagates along a propagation axis;
b) acquiring an image of the sample with the image sensor, the image comprising a plurality of elementary diffraction patterns, each elementary diffraction pattern corresponding to one particle;
c) on the basis of the acquired image, reconstructing a complex image representative of a complex amplitude of the exposure light wave on at least one reconstruction surface passing through the sample, the reconstruction being achieved by implementing an iterative reconstruction algorithm, the algorithm comprising, in each iteration, updating a phase of the exposure light wave in the detection plane or on the reconstruction surface;
d) selecting a region of interest of the complex image, the selected region of interest corresponding to a selected particle of interest;
e) forming an extracted complex image, the extracted complex image being extracted from the region of interest of the complex image selected in d);
f) applying a propagation operator to the extracted complex image formed in e), so as to obtain, in at least one propagation plane, an elementary diffraction pattern of the particle of interest selected in d), such that the elementary diffraction pattern obtained is isolated from elementary diffraction patterns of other particles present in the sample, the elementary diffraction pattern comprising interference fringes; and
g) characterizing the particle of interest depending on the elementary diffraction pattern resulting from f),
wherein g) comprises at least one of:
comparing the elementary diffraction pattern obtained in f), with at least one diffraction pattern corresponding to a known particle;
comparing the elementary diffraction pattern obtained in f), with at least one diffraction pattern modeled in view of a particle the refractive index and/or size of which are known; and
classifying the elementary diffraction pattern obtained in f), in view of diffraction patterns obtained using known particles or diffraction patterns modeled in a training phase.
|