| CPC C23C 14/165 (2013.01) [C22C 21/00 (2013.01); C22C 21/06 (2013.01); C22C 21/10 (2013.01); C22C 21/16 (2013.01); C23C 14/3414 (2013.01); C23C 14/345 (2013.01); C23C 14/3485 (2013.01); C23C 14/35 (2013.01); C23C 14/352 (2013.01); H01J 37/3426 (2013.01); C22F 1/04 (2013.01); H01J 37/3467 (2013.01); Y10T 428/12757 (2015.01)] | 32 Claims |
|
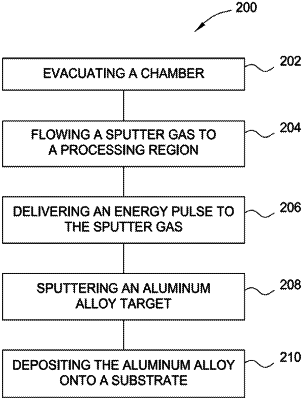
1. A method of magnetron sputtering an aluminum alloy (Currently Amended) coating onto a substrate, the method comprising:
flowing a sputter gas to a processing region of a process chamber, the process chamber having an aluminum alloy sputter target comprising one or more of:
about 1 wt % to about 15 wt % zinc based on the total weight of the alloy,
about 1 wt % to about 10 wt % magnesium based on the total weight of the alloy, or
about 0.1 wt % to about 5 wt % zirconium based on the total weight of the alloy;
applying a magnetic field of about 200 Gauss to about 300 Gauss to the process chamber;
delivering a plurality of energy pulses to the sputter gas, each pulse of the plurality of energy pulses comprising a non-square wave shape, wherein each pulse of the plurality of energy pulses comprises a different amount of power and a different time duration; and
depositing the aluminum alloy coating onto the substrate at a deposition rate of about 2 micrometers per hour to about 3 micrometers per hour by applying a positive target bias voltage of about 200 V to about 1,000 V relative to an anode and a deposition pressure of 4×10−3 mbar to 6×10−3 mbar to produce an alloy coating having a percent total pore volume of about 5% or less and an average pore diameter of about 10 microns or less.
|