| CPC B60L 58/19 (2019.02) [B60L 58/18 (2019.02); B60L 58/20 (2019.02); B60L 58/21 (2019.02); H02J 7/0048 (2020.01); B60L 2240/547 (2013.01); H02J 2310/48 (2020.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A power supply system for an electric vehicle drivetrain, the power supply system comprising:
a first high-voltage battery unit,
a second high-voltage battery unit connected in series with the first high-voltage battery unit,
a circuit arrangement having a plurality of high-power switching semiconductor devices connected to the first and second high-voltage battery units,
an electronic control system configured for controlling operation of the plurality of high-power switching semiconductor devices for:
during a charging mode of the first and second high-voltage battery units, routing high-voltage DC received from a vehicle external charging source alternatingly to the first high-voltage battery unit and to the second high-voltage battery unit, with an alternating frequency of at least 100 Hz, and
during a power supply mode of the power supply system, supplying high-voltage DC from both the first and second high-voltage battery units for driving a vehicle electrical traction machine of the electric vehicle drivetrain, wherein the supplied high-voltage DC has a voltage level corresponding to the accumulated voltage level of the series connected first and second high-voltage battery units
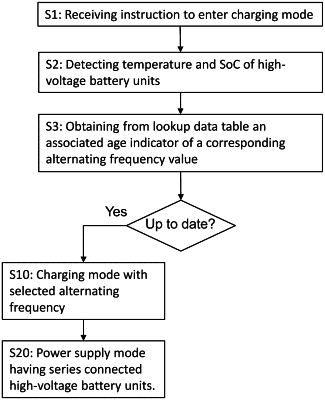
wherein the electronic control system comprises a lookup data table having a plurality of stored data records, each associated with:
a unique combination of a battery state of charge value and a battery temperature value, and
a data field storing a calculated frequency value associated with said unique combination of battery state of charge and battery temperature,
wherein the electronic control system is configured to, upon receiving an instruction to enter the charging mode of the first and second high-voltage battery units, detect current battery temperature level and current battery state of charge of the first and/or second high-voltage battery units, and subsequently use an associated calculated frequency value from the corresponding data record as the alternating frequency.
|