| CPC B60H 1/32284 (2019.05) [B60H 1/3205 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A temperature control system, comprising:
a controller;
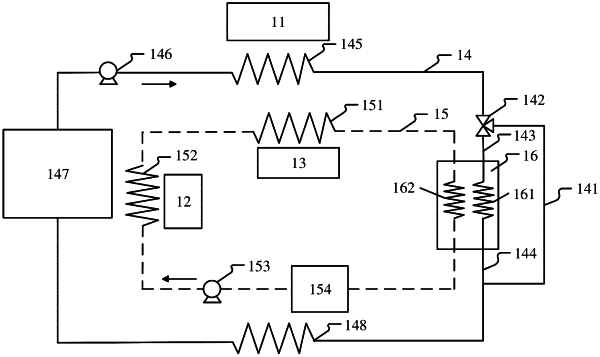
a first cooling circuit, wherein a first cooling medium is circulated in the first cooling circuit, and the first cooling circuit is configured to cool an inverter;
a second cooling circuit, wherein a second cooling medium is circulated in the second cooling circuit, and the second cooling circuit is configured to cool a motor and/or motor speed reducer; and
a heat exchanger, separately connected to the first cooling circuit and the second cooling circuit, and configured to perform heat exchange between the first cooling medium and the second cooling medium, wherein the first cooling circuit comprises a bypass branch and the bypass branch is connected in parallel to the heat exchanger;
wherein a valve is disposed in the first cooling circuit, and the valve is connected to the bypass branch and is configured to control flow distribution of the first cooling medium that flows from a position corresponding to the inverter to the heat exchanger and the bypass branch; and
wherein the inverter is in an electric vehicle, the valve is a controllable valve, and the valve is controlled by the controller and the controller is configured to determine a change that is to occur on heat generation power of the inverter; and
when it is determined that the heat generation power of the inverter is to increase, controlling the valve in a process in which the heat generation power of the inverter increases or before the heat generation power of the inverter increases, so that a percentage of flow that is of the first cooling medium and that flows to the bypass branch is increased.
|