| CPC B60H 1/0073 (2019.05) [B60H 1/00278 (2013.01); B60H 1/00885 (2013.01); B60H 1/00899 (2013.01); B60H 1/3208 (2013.01); B60H 2001/00307 (2013.01); B60H 2001/00949 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
1. A heat control device that is mounted in a vehicle including
a first thermal circuit including a water pump configured to circulate a coolant, a radiator configured to radiate heat of the coolant to an outside of the vehicle, and a radiator fan configured to increase an amount of air passing through the radiator, and
a second thermal circuit including a compressor configured to circulate a refrigerant while changing a state of the refrigerant and to exchange heat with the first thermal circuit,
the heat control device comprising processing circuitry configured to:
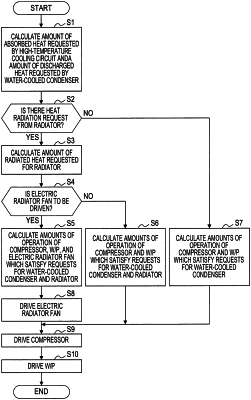
calculate an amount of absorbed heat which is requested by the first thermal circuit and an amount of discharge heat which is requested to be discharged from the second thermal circuit to the first thermal circuit;
determine whether to radiate the heat from the radiator to the outside of the vehicle and whether to drive the radiator fan based on a temperature of a high-temperature coolant and a vehicle speed; and
in response to determining to radiate the heat from the radiator to the outside of the vehicle;
calculate an amount of radiated heat which is requested for the radiator based on the amount of absorbed heat requested by the first thermal circuit and the amount of discharged heat requested by the second thermal circuit;
determine operation amounts of the compressor, the water pump, and the radiator fan such that the operation amounts satisfy the amount of discharged heat of the second thermal circuit and the amount of radiated heat of the radiator, and a sum of power consumption values of the water pump, the compressor, and the radiator fan is minimized;
calculate power consumption values of the compressor and the radiator fan which minimize the sum of the power consumption values of the water pump, the compressor, and the radiator fan under conditions that an amount of discharged heat of the second thermal circuit and an amount of radiated heat of the radiator which are determined by a combination of the power consumption values of the water pump, the compressor, and the radiator fan are respectively equal to or greater than the amount of discharge heat of the second thermal circuit and the amount of radiated heat of the radiator; and
determine the operation amounts of the water pump, the compressor, and the radiator fan such that the power consumption values of the water pump, the compressor, and the radiator fan become the calculated power consumption values.
|