| CPC A61K 35/74 (2013.01) [A61K 35/741 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
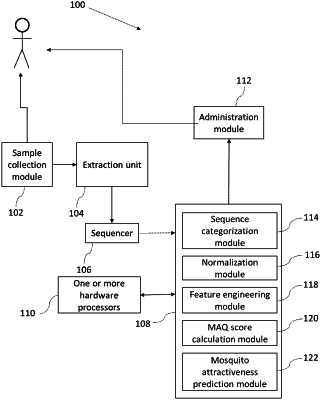
1. A processor implemented method for evaluating and reducing the degree of mosquito-attractiveness of an individual, the method comprising:
collecting a biological sample from skin of the individual, wherein the biological sample is representing skin microbiome of the individual;
extracting, via an extraction unit, microbial nucleic acid content from the collected biological sample;
sequencing the extracted microbial nucleic acid content, via a sequencer, to get sequence data;
categorizing, via one or more hardware processors, the sequenced data into a plurality of taxonomic groups utilizing standardized classification algorithms and a plurality of databases;
computing, via the one or more hardware processors, raw abundance values of a plurality of features, wherein each feature corresponds to a unique taxonomic group from amongst the plurality of taxonomic groups;
normalizing and scaling, via the one or more hardware processors, the computed raw abundance values of each of the plurality of features, wherein the normalizing is configured to adjust the raw abundance values to a common scale, thereby correcting a bias in the computation of the raw abundance values, wherein the bias is due to a plurality of factors;
identifying, via the one or more hardware processors, a set of features amongst the plurality of features based on similarity between a nucleotide sequence corresponding to the feature and the nucleotide sequences corresponding to a set of pre-identified amplicon sequence variants (ASVs), and wherein the set of features is identified if the similarity exceeds a pre-defined range;
performing, via the one or more hardware processors, one or more feature engineering techniques on the normalized and scaled abundance values of the set of features to obtain a collated feature table (CFT), wherein the CFT comprises of a plurality of novel engineered features and their corresponding engineered abundance values;
providing, via the one or more hardware processors, a binary classifier, wherein the binary classifier utilizing a pre-built classification model;
computing, via the one or more hardware processors, a mosquito attractiveness quotient (MAQ) score by feeding the CFT to the binary classifier;
comparing, via the one or more hardware processors, the computed MAQ score with a predefined threshold score, to categorize the individual to be one of a highly attractive or a poorly attractive to mosquitoes; and
administering, via an administration module, skin microbe based therapeutic interventions to the individual, if the individual is categorized as highly attractive to mosquitoes, wherein the therapeutic interventions are configured to:
combat the growth of bacterial groups that metabolize/bio-synthesize sweat and metabolic compounds that are responsible for the production of skin odor that makes the individual attractive to mosquitoes,
aid in the colonization of bacterial groups that improve skin-barrier function and maintain skin health,
aid in degradation of sweat and metabolic compounds that are responsible for the production of skin odor that makes the individual attractive to mosquitoes, or
bio-synthesize sweat and metabolic compounds that are responsible for production of skin odor that makes the individual less attractive to mosquitoes.
|