| CPC A61B 5/1117 (2013.01) [A61B 5/1115 (2013.01); A61B 5/4806 (2013.01); A61B 5/7264 (2013.01); A61B 5/747 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A method of monitoring a patient, the method comprising:
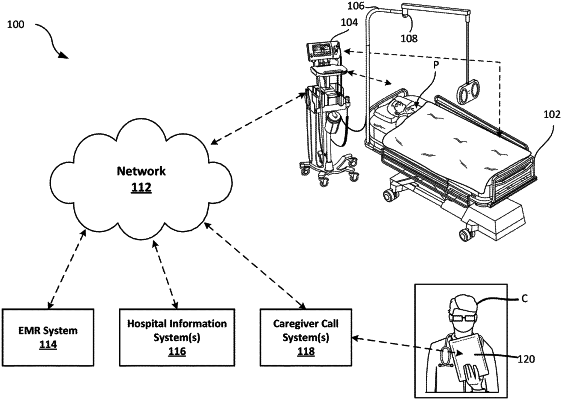
receiving, with a computer vision processor, a video feed of the patient from a video camera at a patient support apparatus in real-time;
analyzing, with the computer vision processor, the video feed to determine one or more postures of the patient relative to the patient support apparatus over time; and
determining, based on the one or more postures, one or more clinical parameters of the patient, wherein the computer vision processor determines how long the patient has been in one position and detects a clinical parameter of sleep of the one or more clinical parameters of the patient when the patient is stationary for a minimum amount of time on the patient support apparatus, wherein the computer vision processor determines how frequently the patient exits the patient support apparatus to detect a clinical parameter of activity of the one or more clinical parameters of the patient, and wherein the computer vision processor determines how often the patient pulls up in the patient support apparatus to detect a clinical parameter of shear of the one or more clinical parameters of the patient, wherein determining how often the patient pulls up in the patient support apparatus includes identifying changes in the one or more postures of the patient relative to an articulation angle of the patient support apparatus to identify friction between the patient and the patient support apparatus;
determining a shear risk score for the patient indicating the patient's likelihood of developing a pressure injury based on the clinical parameter of sleep of the one or more clinical parameters of the patient, the clinical parameter of activity of the one or more clinical parameters of the patient, and the clinical parameter of shear of the one or more clinical parameters of the patient;
issuing a shear alert when the shear risk score exceeds a threshold value;
determining a fall risk score for the patient, based on the one or more clinical parameters of the patient, indicating the patient's likelihood of falling;
withholding a fall alert when the clinical parameter of sleep is detected;
issuing the fall alert when the fall risk score exceeds a threshold value and the one or more clinical parameters indicate the patient is about to exit the patient support apparatus; and
automatically performing a fall risk mitigation action at the patient support apparatus to prevent the patient from exiting the patient support apparatus.
|