| CPC A61B 5/02405 (2013.01) [A61B 5/7225 (2013.01); A61B 5/7257 (2013.01); G16H 40/67 (2018.01); G16H 50/70 (2018.01); A61B 5/02444 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A pulse wave signal analyzer, comprising:
a pulse wave detection unit configured to non-invasively detect a pulse wave signal according to a heartbeat of a living body;
a memory that stores executable instructions; and
a processor configured to execute the instructions such that the processor is configured to:
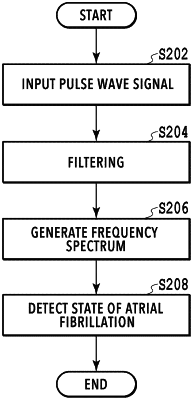
generate a frequency spectrum by performing a Fourier transform of the pulse wave signal detected by a single operation by the pulse wave detection unit for detecting the pulse wave signal; and
detect a state of atrial fibrillation based on the generated frequency spectrum,
wherein when generating the frequency spectrum, the processor is configured to repeatedly perform the Fourier transform of the pulse wave signal over a predetermined time frame while shifting the predetermined time frame in a range of 0.005 seconds to 0.02 seconds for each repeat of the Fourier transform.
|