| CPC H04L 47/20 (2013.01) [H04L 69/16 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A network device comprising:
one or more processors; and
one or more computer-readable non-transitory storage media, the one or more computer-readable non-transitory storage media comprising instructions that, when executed by the one or more processors, cause one or more components of the network device to perform operations comprising:
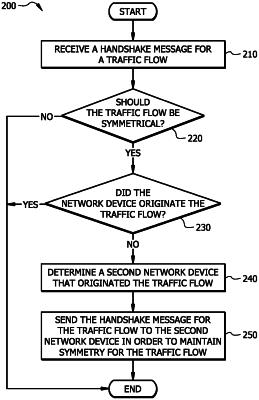
receiving a handshake message for a traffic flow from a Software-Defined Wide-Area Network (SDWAN);
determining, from a traffic policy, whether the traffic flow should be symmetrical;
in response to determining from the traffic policy that the traffic flow should be symmetrical, performing a flow lookup on the traffic flow to determine if the network device originated the traffic flow;
in response to determining that the network device did not originate the traffic flow, determining a second network device that originated the traffic flow; and
sending the handshake message for the traffic flow to the second network device in order to maintain symmetry for the traffic flow.
|