| CPC G06F 30/23 (2020.01) [E21B 41/0057 (2013.01); E21B 2200/20 (2020.05); G06F 2111/10 (2020.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
1. A coupling numerical simulation method for site selection of an underground salt cavern hydrogen storage, comprising operations as follows:
S1: obtaining geological data of an area where the salt cavern hydrogen storage is to be established, wherein the area where the salt cavern hydrogen storage is to be established in S1 is an unexploited salt mine;
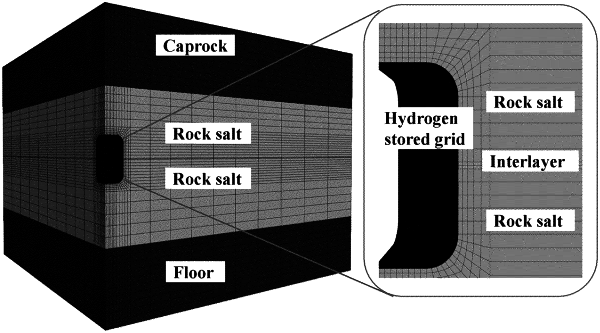
S2: establishing a three-dimensional model and performing grid meshing: establishing a geological model of the area where the single salt cavern hydrogen storage is to be established by using a geo-technical numerical modeling software according to the geological data, and dividing the geological model into computational grids; and performing computational grid densification processing on a peripheral area of a target area of the salt cavern hydrogen storage in the geological model, and selecting a set of computational grids on an inner edge of the target area of the salt cavern hydrogen storage as separate grids;
S3: establishing and balancing an initial coupling field based on the geological model, and then performing excavation simulation of the target area of the salt cavern hydrogen storage in the geological model to obtain a geological model after excavation, wherein an excavation area for excavation simulation of the target area of the salt cavern hydrogen storage in the geological model is an internal area of the separate grid in the target area of the salt cavern hydrogen storage;
S4: importing the geological model after excavation into a multi-phase flow simulation software, and resetting parameter values of the separate grids in the geological model after excavation in the multi-phase flow simulation software, specifically comprising:
increasing a volume of the separate grid to an actual volume of the target area of the salt cavern hydrogen storage to obtain a hydrogen grid; and
setting a porosity of the hydrogen grid to 0.999, setting a permeability to be significantly greater than a permeability of a surrounding rock salt, setting a hydrogen gas saturation to 1.0, and setting other parameters same as computational grids around the hydrogen grid;
S5: coupling a stress model in the geo-technical numerical modeling software with hydraulic and thermal models in the multi-phase flow simulation software, and simulating a stress, hydraulic, and thermal coupling behavior process of a rock layer around the target area of the salt cavern hydrogen storage in the geological model after excavation to obtain a coupled simulation result.
|