| CPC G06F 21/6245 (2013.01) [G06F 9/547 (2013.01); G06F 17/12 (2013.01); G06F 17/18 (2013.01); G06F 21/577 (2013.01); G06F 21/6227 (2013.01)] | 62 Claims |
|
1. A computer implemented data product release method, the method comprising the steps of;
deriving a data product release from a sensitive dataset using a differentially private system, wherein the data product release is a bounded or fixed set of statistics that is (a) predefined by a data holder and (b) derived from the sensitive dataset using the differentially private system, wherein the sensitive dataset includes raw data;
configuring, by the data holder, a prioritization of statistics in the set of statistics, wherein the statistics comprise one or more of a sum, count, average, median, min, or max;
configuring privacy protection parameters of the differentially private system as part of the data product release method to alter the balance between maintaining privacy of the sensitive dataset and making the data product release useful;
wherein the privacy protection parameters comprise a privacy protection parameter epsilon;
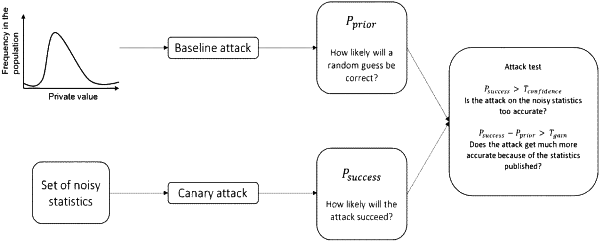
automatically determining a distribution of noise values to be added to the set of statistics by applying multiple different attacks to the set of statistics and by taking into account the prioritization of statistics configured by the data holder;
deriving the set of statistics from the sensitive dataset without providing access to any one or more of the raw data or raw data values within the sensitive dataset; and
directly calculating the privacy protection parameter epsilon from attack characteristics to get the desired attack success.
|