| CPC G01R 33/56375 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0051 (2013.01); A61B 5/055 (2013.01); G01R 33/4818 (2013.01); G01R 33/56358 (2013.01); G06T 11/003 (2013.01); A61B 5/0044 (2013.01); G06T 2210/41 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
1. A method for generating a mechanical property map using a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, the method comprising:
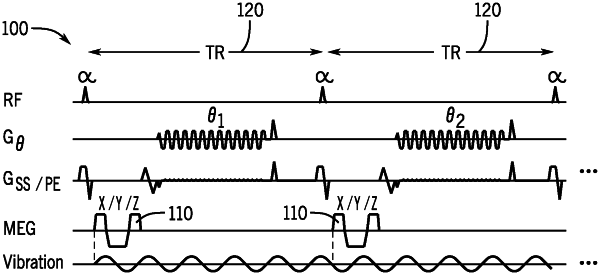
(a) acquiring data from a subject using the MRI system while a vibratory stimulus is provided to the subject in order to induce motion within a tissue of the subject, wherein:
the data are acquired using a pulse sequence that samples k-space in a plurality of planes using an echo planar readout,
each plane is radially rotated about a phase encoding axis in successive repetition time periods of the pulse sequence, and
the pulse sequence includes motion encoding gradients that are generated before each echo planar readout in order to encode the motion within the tissue into an image phase of the data;
wherein the data are acquired with uniform undersampling in a through-plane dimension;
(b) reconstructing a plurality of images from the data using an iterative sparsity regularized image reconstruction technique based on a signal model that includes a forward operator that accounts for the uniform undersampling in the through-plane dimension, wherein the reconstructed images are indicative of the image phase into which the motion within the tissue has been encoded; and
(c) generating a mechanical property map from the reconstructed images.
|