| CPC G01R 31/086 (2013.01) [G01R 25/00 (2013.01); H02H 1/0007 (2013.01); H02H 7/22 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
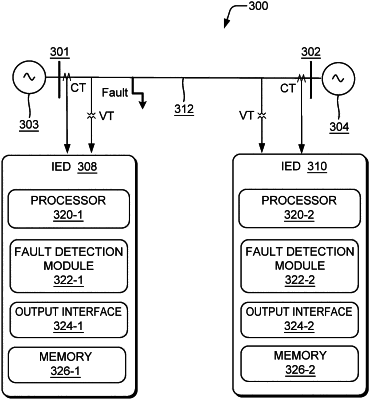
10. An intelligent electronic device (IED) to detect a fault during a power swing in a power transmission line, the IED comprising:
a processor; and
a fault detection module executable by the processor to:
obtain voltage measurements and current measurements from each phase at a terminal of the power transmission system, wherein the voltage measurements and the current measurements are obtained with one or more measurement equipment associated with the terminal of the power transmission system, wherein the voltage measurements and the current measurements comprise samples of voltage and current values obtained at the terminal;
calculate, for each sample of the voltage and current values, a value of change in an impedance angle for each phase-to-ground loop and each phase-to-phase loop, wherein the value of change in the impedance angle is a difference between impedance angles of two samples separated by a predetermined interval;
calculate average values for change in impedance angle for a predetermined number of values of the change in the impedance angles, for each phase-to-ground loop and each phase-to-phase loop;
compare the average values calculated for each phase-to-ground loop and each phase-to-phase loop with a threshold range of change in impedance angle; and
detect a fault in one or more of the phase-to-ground loops or phase-to-phase loops when the average value calculated for the one or more phase-to-ground loops or phase-to-phase loops is within the threshold range.
|