|
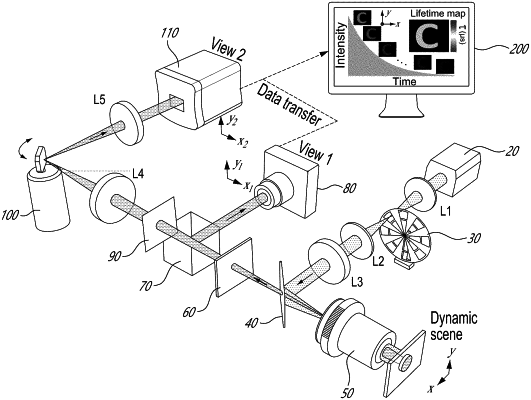
1. A method for real-time wide-field dynamic temperature sensing of an object, comprising producing wide-field illumination to upconverting nanoparticles at the object plane, collecting a light emitted by the upconverting nanoparticles, dividing a collected light into a reflected component and a transmitted component; imaging the reflected component into a first image, imaging the transmitted component into a second image; processing the images; reconstruction datacubes of the object from resulting processed images; and converting the reconstructed datacube to photoluminescence lifetime maps and temperature distributions, wherein said imaging the transmitted component comprises spatial encoding the object into spatially encoded frames using one of: a printed mask and a static mask displayed by a spatial light modulator, the method comprising temporally shearing the spatially encoded frames using a rotating mirror, and spatiotemporal integration of resulting spatially encoded and temporally sheared object into the second image.
|