| CPC F25B 41/20 (2021.01) [F25B 49/02 (2013.01); F25B 2400/0401 (2013.01); F25B 2400/0409 (2013.01); F25B 2600/2501 (2013.01); F25B 2700/2117 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
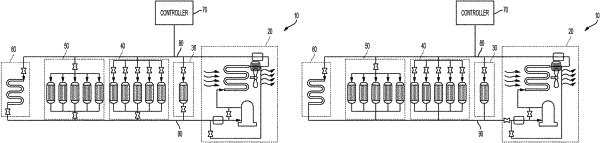
1. A method of maintaining a uniform isothermal temperature distribution on at least one cold plate having highly transient thermal loads thereon by utilizing a vapor compression apparatus having a supply line and a return line connected to the cold plate and using a compressor to draw a vapor working fluid from the at least one cold plate in order to compress the vapor working fluid and supply a compressed higher-pressure refrigerant to a condenser and the condenser to condense the working fluid to a liquid that flows to the at least one cold plate via the supply line and evaporates in the at least one cold plate to remove the heat load supplied to the at least one cold plate from the highly transient thermal loads, and returning a lower-pressure fluid vapor to the inlet of the compressor via the return line, and a controller, wherein the controller is configured to execute the method comprising:
a. adjusting a bypass of fluid flow directly back to the compressor suction from the compressor discharge or adjusting the speed of the compressor to maintain a necessary compressor suction pressure responding to varying flow demands from the cold plate;
b. adjusting a bypass of fluid flow around the at least one cold plate to control the superheat at the compressor suction;
c. adjusting the flow of fluid through the at least one cold plate to maintain a desired superheat of fluid exiting the at least one cold plate to accommodate varying heat loads; and
d. adjusting the opening of a cold plate outlet valve in the at least one cold plate exit flow path to maintain a desired saturation temperature in the at least one cold plate by adjusting pressure of the fluid in the exit flow path;
wherein adjusting the flow of fluid through the at least one cold plate with multiple parallel passages is to maintain balanced flow rate among the multiple parallel passages and also maintain the desired superheat of a fluid leaving the multiple parallel passages after being recombined into a single flow from the cold plate exit is through the adjustment of the superheat temperature by throttling of an expansion valve at the inlet to all the passages of a cold plate, where each passage has an additional flow restriction or orifice to create a flow condition wherein the refrigerant is a single phase fluid between the single expansion valve and the multiple parallel passages to ensure a near uniform refrigeration flow rate between each channel by means of the additional flow restriction or the orifice.
|