| CPC F01N 3/2073 (2013.01) [F01N 3/0814 (2013.01); F01N 3/206 (2013.01); G06F 18/214 (2023.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A method for a vehicle, comprising:
acquiring measurements from at least one exhaust emission sensor of the vehicle, the at least one exhaust emission sensor positioned to measure one or more of NOx, NH3, and O2 levels in exhaust gas of the vehicle, wherein the acquiring includes obtaining a signal representing an ammonia concentration in the exhaust gas and subtracting the signal representing the ammonia concentration from a total linear oxygen signal of the at least one exhaust emission sensor, and wherein subtracting the signal representing the ammonia concentration from the total linear oxygen signal includes generating a first value representing a first sum of a CO concentration, a hydrogen concentration, and a hydrocarbon concentration in the exhaust gas;
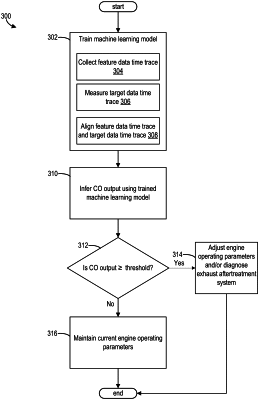
inputting the measurements from the at least one exhaust emission sensor into a machine learning model trained to output a predicted real-time amount of at least one exhaust gas constituent, the at least one exhaust gas constituent including CO and/or hydrocarbons; and
adjusting and assessing operations of an emissions aftertreatment system based on the predicted real-time amount of the at least one exhaust gas constituent.
|